Page 43 - Read Online
P. 43
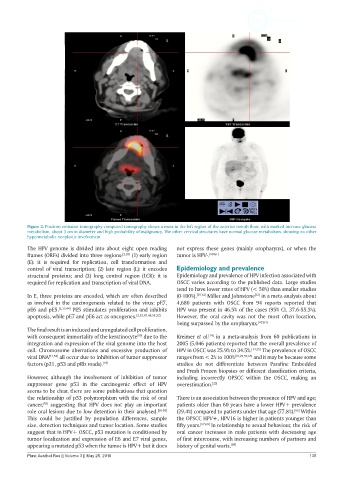
Figure 2: Positron emission tomography-computed tomography shows a mass in the left region of the anterior mouth floor, with marked increase glucose
metabolism, about 3 cm in diameter and high probability of malignancy. The other cervical structures have normal glucose metabolism, showing no other
hypermetabolic neoplastic involvement
The HPV genome is divided into about eight open reading not express these genes (mainly oropharynx), or when the
frames (ORFs) divided into three regions: [2,33] (1) early region tumor is HPV-. [60,61]
(E): it is required for replication, cell transformation and
control of viral transcription; (2) late region (L): it encodes Epidemiology and prevalence
structural proteins; and (3) long control region (LCR): it is Epidemiology and prevalence of HPV infection associated with
required for replication and transcription of viral DNA. OSCC varies according to the published data. Large studies
tend to have lower rates of HPV (< 50%) than smaller studies
[33]
In E, three proteins are encoded, which are often described (0-100%). [25,62] Miller and Johnstone in a meta-analysis about
as involved in the carcinogenesis related to the virus: pE7, 4,680 patients with OSCC from 94 reports reported that
pE6 and pE5. [2,33,44] PE5 stimulates proliferation and inhibits HPV was present in 46.5% of the cases (95% CI, 37.6-55.5%).
apoptosis, while pE7 and pE6 act as oncogenes. [2,33,47,48,51,52] However, the oral cavity was not the most often location,
being surpassed by the oropharynx. [63,64]
The final result is an induced and unregulated cell proliferation,
with consequent immortality of the keratinocyte due to the Kreimer et al. in a meta-analysis from 60 publications in
[14]
[19]
integration and expression of the viral genome into the host 2005 (5,046 patients) reported that the overall prevalence of
cell. Chromosome aberrations and excessive production of HPV in OSCC was 25.9% to 34.5%. [14,25] The prevalence of OSCC
viral DNA [53,54] all occur due to inhibition of tumor suppressor ranges from < 2% to 100% [10,25,57,65] and it may be because some
factors (p21, p53 and pRb roads). [19] studies do not differentiate between Parafine Embedded
and Fresh Frozen biopsies or different classification criteria,
However, although the involvement of inhibition of tumor including incorrectly OPSCC within the OSCC, making an
suppressor gene p53 in the carcinogenic effect of HPV overestimation. [25]
seems to be clear, there are some publications that question
the relationship of p53 polymorphism with the risk of oral There is an association between the presence of HPV and age;
cancer, suggesting that HPV does not play an important patients older than 60 years have a lower HPV+ prevalence
[55]
role oral lesions due to low detention in their analysed. [56-59] (29.4%) compared to patients under that age (77.8%). Within
[66]
This could be justified by population differences, sample the OPSCC HPV+, HPV16 is higher in patients younger than
size, detection techniques and tumor location. Some studies fifty years. [67,68] In relationship to sexual behaviour, the risk of
suggest that in HPV+ OSCC, p53 mutation is conditioned by oral cancer increases in male patients with decreasing age
tumor localization and expression of E6 and E7 viral genes, of first intercourse, with increasing numbers of partners and
appearing a mutated p53 when the tumor is HPV+ but it does history of genital warts. [69]
Plast Aesthet Res || Volume 3 || May 25, 2016 135