Page 44 - Read Online
P. 44
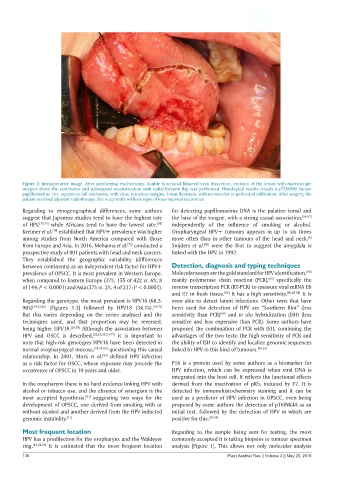
Figure 3: Intraoperative image. After performing tracheotomy, double functional bilateral neck dissection, excision of the lesion with macroscopic
margins above the centimeter and subsequent reconstruction with radial forearm flap was performed. Histological results reveals a pT3N0M0 human
papillomavirus 16+ squamous cell carcinoma, with close resection margins, 6 mm thickness, with no vascular or perineural infiltration. After surgery, the
patient received adjuvant radiotherapy. She is currently without signs of loco-regional recurrence
Regarding to etnogeographical differences, some authors for detecting papillomavirus DNA is the palatine tonsil and
suggest that Japanese studies tend to have the highest rate the base of the tongue, with a strong causal association, [14,82]
[59]
of HPV, [70,71] while Africans tend to have the lowest rate. independently of the influence of smoking or alcohol.
Kreimer et al. established that HPV+ prevalence was higher Oropharyngeal HPV+ tumours appears in up to six times
[14]
among studies from North America compared with those more often than in other tumours of the head and neck.
[6]
from Europe and Asia. In 2016, Mehanna et al. conducted a Snijders et al. were the first to suggest the amygdala is
[72]
[83]
prospective study of 801 patients with head and neck cancers. linked with the HPV, in 1992.
They established the geographic variability (differences
between continents) as an independent risk factor for HPV+ Detection, diagnosis and typing techniques
prevalence of OPSCC. It is most prevalent in Western Europe, Molecular assays are the gold standard for HPV identification,
[84]
[85]
when compared to Eastern Europe (37%, 155 of 422 vs. 6%, 8 mainly polymerase chain reaction (PCR), specifically the
of 144; P < 0.0001) and Asia (37% vs. 2%, 4 of 217; P < 0.0001). reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR) to measure viral mRNA E6
and E7 in fresh tissue. It has a high sensitivity. [80,85-88] It is
[86]
Regarding the genotype, the most prevalent is HPV16 (68.2- even able to detect latent infections. Other tests that have
90%) [14,33,66] [Figures 1-3] followed by HPV18 (34.1%). [14,73] been used for detection of HPV are “Southern Blot” (less
[89]
But this varies depending on the series analysed and the sensitivity than PCR) and in situ hybridization (ISH) (less
techniques used, and that proportion may be reversed, sensitive and less expensive than PCR). Some authors have
being higher HPV18. [28,59] Although the association between proposed the combination of PCR with ISH, combining the
HPV and OSCC is described, [32,62,68,74-77] it is important to advantages of the two tests: the high sensitivity of PCR and
note that high-risk genotypes HPV16 have been detected in the ability of ISH to identify and localize genomic sequences
normal oropharyngeal mucosa, [78,79,62] questioning this causal linked to HPV in this kind of tumours. [90,91]
[80]
relationship. In 2001, Mork et al. defined HPV infection
as a risk factor for OSCC, whose exposure may precede the P16 is a protein used by some authors as a biomarker for
occurrence of OPSCC in 10 years and older. HPV infection, which can be expressed when viral DNA is
integrated into the host cell. It reflects the functional effects
In the oropharynx there is no hard evidence linking HPV with derived from the inactivation of pRb, induced by E7. It is
alcohol or tobacco use, and the absence of synergism is the detected by immunohistochemistry staining and it can be
most accepted hypothesis, suggesting two ways for the used as a predictor of HPV infection in OPSCC, even being
[81]
development of OPSCC, one derived from smoking with or proposed by some authors the detection of p16INK4A as an
without alcohol and another derived from the HPV inducted initial test, followed by the detection of HPV in which are
genomic instability. [31] positive for this. [92-94]
Most frequent location Regarding to the sample being sent for testing, the most
HPV has a predilection for the oropharynx and the Waldeyer commonly accepted it is taking biopsies or tumour specimen
ring. [14,24,59] It is estimated that the most frequent location analysis [Figure 1]. This allows not only molecular analysis
136 Plast Aesthet Res || Volume 3 || May 25, 2016