Page 109 - Read Online
P. 109
Muroy et al. Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation 2020;7:166-82 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-8659.2020.16 Page 177
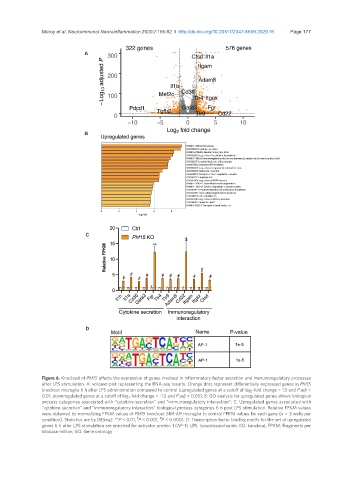
Figure 6. Knockout of Phf15 affects the expression of genes involved in inflammatory factor secretion and immunoregulatory processes
after LPS stimulation. A: volcano plot representing the RNA-seq results. Orange dots represent differentially expressed genes in Phf15
knockout microglia 6 h after LPS administration compared to control (upregulated genes at a cutoff of log 2 -fold change > 1.5 and P adj <
0.01; downregulated genes at a cutoff of log 2 -fold change < -1.5 and P adj < 0.05); B: GO analysis for upregulated genes shows biological
process categories associated with “cytokine secretion” and “immunoregulatory interaction”; C: Upregulated genes associated with
“cytokine secretion” and “immunoregulatory interaction” biological process categories 6 h post LPS stimulation. Relative FPKM values
were obtained by normalizing FPKM values of Phf15 knockout SIM-A9 microglia to control FPKM values for each gene (n = 3 wells per
$
#
condition). Statistics are by DESeq2: **P < 0.01, P < 0.001, P < 0.0001; D: Transcription factor binding motifs for the set of upregulated
genes 6 h after LPS stimulation are enriched for activator protein 1 (AP-1). LPS: lipopolysaccharide; KO: knockout; FPKM: Fragments per
kilobase million; GO: Gene ontology