Page 192 - Read Online
P. 192
Lai et al. Imbalance of NK and B cell subsets in GMG exacerbation
percentage of Bregs did not differ between the patients antibodies suggest altered immunity, but any single
in exacerbation with infections (6.84 ± 1.59) and those antibody determination is hardly reflective of the
without infections (7.05 ± 1.85). progression or activity of the disease. The production
of the above-mentioned antibodies are likely the result
DISCUSSION of the dysfunctioned lymphocytes, thus measuring
the peripheral lymphocytes subsets in MG patients
Disorders of neuromuscular junction can be of may be a promising way to monitor the progression
immunological, toxic, or genetic origin; and among of the disease.
these rare disorders, MG is the most common. The
clinical hallmark of MG is a fluctuating weakness and B cell abnormalities contribute to the development
fatigability of the affected voluntary muscles. With the and progress of autoimmune diseases. Traditionally,
advent of immunotherapy, the long-term outcome has the predominant function of B cells was thought to
been improved significantly, [39] but the symptomatic be limited to production of autoantibodies. However,
deterioration after symptomatic remission takes B cells have both positive and negative regulatory
places in majority of MG patients including both the roles during immune responses. During murine
OMG and GMG cases. [40-42] Thus, reliable markers development the absence of B cells results in
that reflect the activity of the disease to guide the significant quantitative and qualitative abnormalities
clinical therapy are critical. within the immune system, including a remarkable
decrease in thymocytes numbers, defects within
[44]
MG patients present with heterogeneous clinical spleen dendritic cells and T cells compartments. [45,46]
patterns in terms of onset-age, initial symptoms, mode Through production of immunomodulatory cytokines,
of development, thymic abnormalities, immunological B cells can also negatively regulate cellular immune
profiles, and responsiveness to treatment. MG is responses. A variety of regulatory B cell subsets
currently considered to consist of a heterogeneous have been described. Whether Breg cells can serve
group of autoimmune diseases, which share common as a marker for disease activity in MG remains to
aspects, such as the impairment of neuromuscular be determined. Our observation showed that the
transmission induced by autoimmunity, manifested by percentage of Breg cells was significantly decreased
muscle weakness and fatigability and the response to in the peripheral blood of GMG patients, indicating that
both pyridostigmine and immunosuppressants. [43] Breg cells are affected during the development of the
disease. But when we further focused on the changes
In MG, the presence of multiple autoantibodies against of Breg cells between the two subgroups of GMG, no
numerous targeted molecules (e.g. AChR-ab). These
significant difference was found between them. This
interesting finding suggests that the peripheral Breg
cells dysfunction may contribute to the development
of MG, but are likely not a main factor in the acute
exacerbation of disease. Thus, more detailed studies
on the subsets of Breg cells may provide valuable
insights into the role of Breg cells in MG.
NK cells are large granular cells that constitute
5-10% of circulating lymphocytes in humans, and are
important effectors in innate immunity. Increasing
[29]
studies report that NK cells can also act as regulators
in adaptive immunity by producing cytokines which
modulate the downstream immune factors. [47-49] In
addition, NK cells were found to play a protective
role in several autoimmune disease models. [50-52] In
EAMG, Liu et al. reported that NK cells proliferate
[53]
in the early stages of the disease; the percentage
of NK cells then decrease with disease progression.
Based on the observations, NK cells were suggested
+
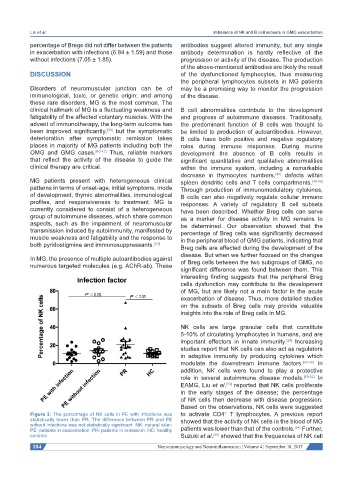
Figure 3: The percentage of NK cells in PE with infections was to activate CD4 T lymphocytes. A previous report
statistically lower than PR. The difference between PR and PE showed that the activity of NK cells in the blood of MG
without infections was not statistically significant. NK: natural killer; [54]
PE: patients in exacerbation; PR: patients in remission; HC: healthy patients was lower than that of the controls. Further,
controls Suzuki et al. showed that the frequencies of NK cell
[55]
184 Neuroimmunology and Neuroinflammation ¦ Volume 4 ¦ September 18, 2017