Page 278 - Read Online
P. 278
Chen MAGL in neurodegenerative diseases
disruption of MAGL would be a promising strategy like neurodegenerative disease or to halt progression
to enhance anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective of diseases. Earlier studies show that 2-AG protects
2-AG signaling, while reducing proinflammatory and neurons against brain trauma in a mouse model of
[7]
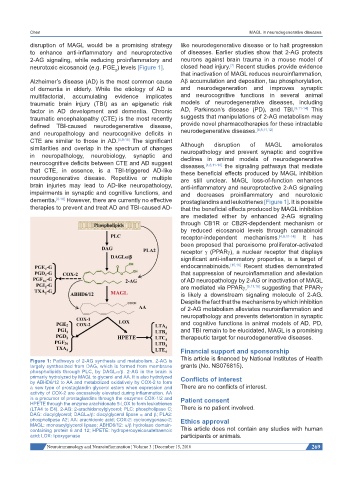
neurotoxic eicosanoid (e.g. PGE ) levels [Figure 1]. closed head injury. Recent studies provide evidence
2
that inactivation of MAGL reduces neuroinflammation,
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common cause Aβ accumulation and deposition, tau phosphorylation,
of dementia in elderly. While the etiology of AD is and neurodegeneration and improves synaptic
multifactorial, accumulating evidence implicates and neurocognitive functions in several animal
traumatic brain injury (TBI) as an epigenetic risk models of neurodegenerative diseases, including
factor in AD development and dementia. Chronic AD, Parkinson’s disease (PD), and TBI. [8,11-14] This
traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) is the most recently suggests that manipulations of 2-AG metabolism may
defined TBI-caused neurodegenerative disease, provide novel pharmacotherapies for these intractable
[4,8,11,12]
and neuropathology and neurocognitive deficits in neurodegenerative diseases.
CTE are similar to those in AD. [4,8-10] The significant Although disruption of MAGL ameliorates
similarities and overlap in the spectrum of changes neuropathology and prevent synaptic and cognitive
in neuropathology, neurobiology, synaptic and declines in animal models of neurodegenerative
neurocognitive deficits between CTE and AD suggest diseases, [4,8,11-14] the signaling pathways that mediate
that CTE, in essence, is a TBI-triggered AD-like these beneficial effects produced by MAGL inhibition
neurodegenerative disease. Repetitive or multiple are still unclear. MAGL loss-of-function enhances
brain injuries may lead to AD-like neuropathology, anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective 2-AG signaling
impairments in synaptic and cognitive functions, and and decreases proinflammatory and neurotoxic
dementia. [8-10] However, there are currently no effective prostaglandins and leukotrienes [Figure 1]. It is possible
therapies to prevent and treat AD and TBI-caused AD- that the beneficial effects produced by MAGL inhibition
are mediated either by enhanced 2-AG signaling
through CB1R or CB2R-depdendent mechanism or
by reduced eicosanoid levels through cannabinoid
receptor-independent mechanisms. [4,8,11-14] It has
been proposed that peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor γ (PPARγ), a nuclear receptor that displays
significant anti-inflammatory properties, is a target of
endocannabinoids. [15,16] Recent studies demonstrated
that suppression of neuroinflammation and alleviation
of AD neuropathology by 2-AG or inactivation of MAGL
are mediated via PPARγ, [5,11,16] suggesting that PPARγ
is likely a downstream signaling molecule of 2-AG.
Despite the fact that the mechanisms by which inhibition
of 2-AG metabolism alleviates neuroinflammation and
neuropathology and prevents deterioration in synaptic
and cognitive functions in animal models of AD, PD,
and TBI remain to be elucidated, MAGL is a promising
therapeutic target for neurodegenerative diseases.
Financial support and sponsorship
This article is financed by National Institutes of Health
Figure 1: Pathways of 2-AG synthesis and metabolism. 2-AG is
largely synthesized from DAG, which is formed from membrane grants (No. NS076815).
phospholipids through PLC, by DAGLα/β. 2-AG in the brain is
primarily hydrolyzed by MAGL to glycerol and AA. It is also hydrolyzed Conflicts of interest
by ABHD6/12 to AA and metabolized oxidatively by COX-2 to form
a new type of prostaglandin glycerol esters when expression and There are no conflicts of interest.
activity of COX-2 are excessively elevated during inflammation. AA
is a precursor of prostaglandins through the enzymes COX-1/2 and Patient consent
HPETE through the enzyme arachidonate 5-LOX to form leukotrienes
(LTA4 to E4). 2-AG: 2-arachidonoylglycerol; PLC: phospholipase C; There is no patient involved.
DAG: diacylglycerol; DAGLα/β: diacylglycerol lipase α and β; PLA2:
phospholipase A2; AA: arachidonic acid; COX-2: cyclooxygenase-2; Ethics approval
MAGL: monoacylglycerol lipase; ABHD6/12: α/β hydrolase domain-
containing protein 6 and 12; HPETE: hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoic This article does not contain any studies with human
acid; LOX: lipoxygenase participants or animals.
Neuroimmunology and Neuroinflammation ¦ Volume 3 ¦ December 15, 2016 269