Page 218 - Read Online
P. 218
Konsman Immune-brain circuits and behavior
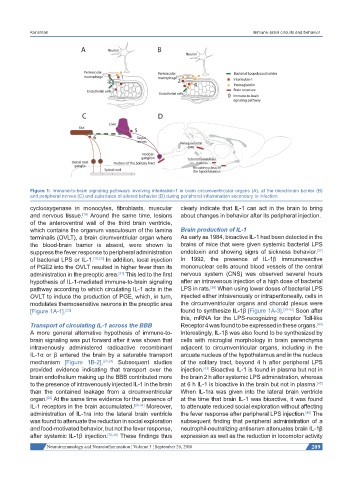
Figure 1: Immune-to-brain signaling pathways involving interleukin-1 in brain circumventricular organs (A), at the blood-brain barrier (B)
and peripheral nerves (C) and substrates of altered behavior (D) during peripheral inflammation secondary to infection
cyclooxygenase in monocytes, fibroblasts, muscular clearly indicate that IL-1 can act in the brain to bring
and nervous tissue. Around the same time, lesions about changes in behavior after its peripheral injection.
[18]
of the anteroventral wall of the third brain ventricle,
which contains the organum vasculosum of the lamina Brain production of IL-1
terminalis (OVLT), a brain cirumventriular organ where As early as 1984, bioactive IL-1 had been detected in the
the blood-brain barrier is absent, were shown to brains of mice that were given systemic bacterial LPS
[37]
suppress the fever response to peripheral administration endotoxin and showing signs of sickness behavior.
of bacterial LPS or IL-1. [19,20] In addition, local injection In 1992, the presence of IL-1β immunoreactive
of PGE2 into the OVLT resulted in higher fever than its mononuclear cells around blood vessels of the central
administration in the preoptic area. This led to the first nervous system (CNS) was observed several hours
[21]
hypothesis of IL-1-mediated immune-to-brain signaling after an intravenous injection of a high dose of bacterial
[38]
pathway according to which circulating IL-1 acts in the LPS in rats. When using lower doses of bacterial LPS
OVLT to induce the production of PGE, which, in turn, injected either intravenously or intraperitoneally, cells in
modulates thermosensitive neurons in the preoptic area the circumventricular organs and choroid plexus were
[Figure 1A-1]. [22] found to synthesize IL-1β [Figure 1A-3]. [39-43] Soon after
this, mRNA for the LPS-recognizing receptor Toll-like
Transport of circulating IL-1 across the BBB Receptor 4 was found to be expressed in these organs.
[44]
A more general alternative hypothesis of immune-to- Interestingly, IL-1β was also found to be synthesized by
brain signaling was put forward after it was shown that cells with microglial morphology in brain parenchyma
intravenously administered radioactive recombinant adjacent to circumventricular organs, including in the
IL-1α or β entered the brain by a saturable transport arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus and in the nucleus
mechanism [Figure 1B-2]. [23,24] Subsequent studies of the solitary tract, beyond 4 h after peripheral LPS
provided evidence indicating that transport over the injection. Bioactive IL-1 is found in plasma but not in
[43]
brain endothelium making up the BBB contributed more the brain 2 h after systemic LPS administration, whereas
to the presence of intravenously injected IL-1 in the brain at 6 h IL-1 is bioactive in the brain but not in plasma.
[45]
than the contained leakage from a circumventricular When IL-1ra was given into the lateral brain ventricle
organ. At the same time evidence for the presence of at the time that brain IL-1 was bioactive, it was found
[25]
IL-1 receptors in the brain accumulated. [26-34] Moreover, to attenuate reduced social exploration without affecting
administration of IL-1ra into the lateral brain ventricle the fever response after peripheral LPS injection. The
[46]
was found to attenuate the reduction in social exploration subsequent finding that peripheral administration of a
and food-motivated behavior, but not the fever response, neutrophil-neutralizing antiserum attenuates brain IL-1β
after systemic IL-1β injection. [35,36] These findings thus expression as well as the reduction in locomotor activity
Neuroimmunology and Neuroinflammation ¦ Volume 3 ¦ September 26, 2016 209