Page 121 - Read Online
P. 121
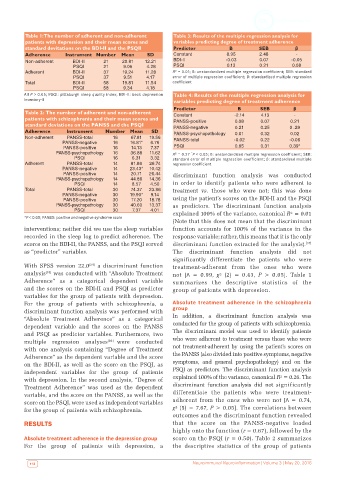
Table 1: The number of adherent and non-adherent Table 3: Results of the multiple regression analysis for
patients with depression and their mean scores and variables predicting degree of treatment adherence
standard devitations on the BDI-II and the PSQII Predictor B SEB β
Adherence Instrument Number Mean SD Constant 8.95 2.48 -
Non-adherent BDI-II 21 20.81 12.21 BDI-II -0.03 0.07 -0.05
PSQI 21 9.05 4.28 PSQI 0.13 0.21 0.08
Adherent BDI-II 37 19.24 11.28 R² = 0.01; B: unstandardized multiple regression coefficient; SEB: standard
PSQI 37 9.51 4.17 error of multiple regression coefficient; β: standardized multiple regression
Total BDI-II 58 19.81 11.54 coefficient
PSQI 58 9.34 4.18
All P > 0.05; PSQI: pittsburgh sleep quality index; BDI-II: beck depression Table 4: Results of the multiple regression analysis for
inventory-II variables predicting degree of treatment adherence
Predictor B SEB β
Table 2: The number of adherent and non-adherent Constant -2.14 4.13 -
patients with schizophrenia and their mean scores and PANSS-positive 0.08 0.07 0.21
standard deviations on the PANSS and the PSQI PANSS-negative 0.21 0.25 0 .29
Adherence Instrument Number Mean SD PANSS-psychopathology 0.01 0.32 0.02
Non-adherent PANSS-total 16 67.81 19.56 PANSS-total -0.02 0.22 -0.06
PANSS-negative 16 16.81* 6.76
PANSS-positive 16 14.13 7.37 PSQI 0.65 0.31 0.39*
PANSS-psychopathology 16 36.88 11.62 R² = 0.27 P < 0.05; B: unstandardized multiple regression coefficient; SEB:
*
PSQI 16 6.31 3.32 standard error of multiple regression coefficient; β: standardized multiple
Adherent PANSS-total 14 81.86 26.74 regression coefficient
PANSS-negative 14 23.43* 10.42
PANSS-positive 14 20.71 26.44 discriminant function analysis was conducted
PANSS-psychopathology 14 44.86 14.36
PSQI 14 8.57 4.50 in order to identify patients who were adherent to
Total PANSS-total 30 74.37 23.86 treatment vs. those who were not; this was done
PANSS-negative 30 19.90* 9.14
PANSS-positive 30 17.20 18.78 using the patient’s scores on the BDI-II and the PSQI
PANSS-psychopathology 30 40.60 13.37 as predictors. The discriminant function analysis
PSQI 30 7.37 4.01 explained 100% of the variance, canonical R² = 0.01
*P < 0.05; PANSS: positive and negative syndrome scale
(Note that this does not mean that the discriminant
interventions; neither did we use the sleep variables function accounts for 100% of the variance in the
recorded in the sleep log to predict adherence. The response variable; rather, this means that it is the only
scores on the BDI-II, the PANSS, and the PSQI served discriminant function extracted for the analysis). [37]
as “predictor” variables. The discriminant function analysis did not
significantly differentiate the patients who were
With SPSS version 22.0 [34] a discriminant function treatment-adherent from the ones who were
analysis [35] was conducted with “Absolute Treatment not [Λ = 0.99, χ² (2) = 0.43, P > 0.05]. Table 1
Adherence” as a categorical dependent variable summarizes the descriptive statistics of the
and the scores on the BDI-II and PSQI as predictor group of patients with depression.
variables for the group of patients with depression.
For the group of patients with schizophrenia, a Absolute treatment adherence in the schizophrenia
discriminant function analysis was performed with group
“Absolute Treatment Adherence” as a categorical In addition, a discriminant function analysis was
dependent variable and the scores on the PANSS conducted for the group of patients with schizophrenia.
and PSQI as predictor variables. Furthermore, two The discriminant model was used to identify patients
multiple regression analyses [36] were conducted who were adherent to treatment versus those who were
with one analysis containing “Degree of Treatment not treatment-adherent by using the patient’s scores on
Adherence” as the dependent variable and the score the PANSS (also divided into positive symptoms, negative
on the BDI-II, as well as the score on the PSQI, as symptoms, and general psychopathology) and on the
independent variables for the group of patients PSQI as predictors. The discriminant function analysis
with depression. In the second analysis, “Degree of explained 100% of the variance, canonical R² = 0.26. The
Treatment Adherence” was used as the dependent discriminant function analysis did not significantly
variable, and the score on the PANSS, as well as the differentiate the patients who were treatment-
score on the PSQI, were used as independent variables adherent from the ones who were not [Λ = 0.74,
for the group of patients with schizophrenia. χ² (5) = 7.67, P > 0.05]. The correlations between
outcomes and the discriminant function revealed
RESULTS that the score on the PANSS-negative loaded
highly onto the function (r = 0.67), followed by the
Absolute treatment adherence in the depression group score on the PSQI (r = 0.50). Table 2 summarizes
For the group of patients with depression, a the descriptive statistics of the group of patients
112 Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation | Volume 3 | May 20, 2016