Page 191 - Read Online
P. 191
CASE REPORT simultaneous amplification of the “syndrome specific
signature genes” of all the probable causative agents,
A 32-year-old male presented with headache, vomiting, followed by “syndrome specific hybridization”.
fever, and focal seizures involving the right upper
limb of 1-week duration. There was no significant Based on a presumptive diagnosis of HSE, the patient was
past history. There was no history suggestive of any started on intravenous acyclovir (500 mg 8th hourly).
immunodeficiency. On examination, the patient was He was also started on anti-cerebral edema medications,
hemodynamically stable and conscious but febrile intravenous 20% mannitol 150 mL 6th hourly, and
and irritable. He had no focal neurological deficits steroids (dexamethasone) 8 mg 8th hourly. His
but had signs of meningeal irritation. The pupils were sensorium deteriorated soon after admission, being
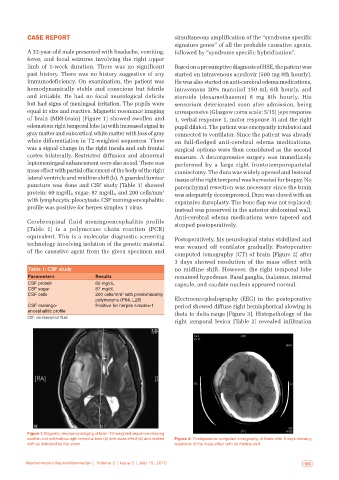
equal in size and reactive. Magnetic resonance imaging unresponsive (Glasgow coma scale: 5/15) (eye response
of brain (MRI-brain) [Figure 1] showed swollen and 1, verbal response 1, motor response 3) and the right
edematous right temporal lobe (a) with increased signal in pupil dilated. The patient was emergently intubated and
gray matter and subcortical white matter with loss of gray connected to ventilator. Since the patient was already
white differentiation in T2-weighted sequences. There on full-fledged anti-cerebral edema medications,
was a signal change in the right insula and sub frontal surgical options were then considered as the second
cortex bilaterally. Restricted diffusion and abnormal measure. A decompressive surgery was immediately
leptomeningeal enhancement were also noted. There was performed by a large right frontotemporoparietal
mass effect with partial effacement of the body of the right craniectomy. The dura was widely opened and lesional
lateral ventricle and midline shift (b). A guarded lumbar tissue of the right temporal was harvested for biopsy. No
puncture was done and CSF study [Table 1] showed parenchymal resection was necessary since the brain
3
protein: 60 mg/dL, sugar: 87 mg/dL, and 200 cells/mm was adequately decompressed. Dura was closed with an
with lymphocytic pleocytosis. CSF meningoencephalitic expansive duroplasty. The bone flap was not replaced;
profile was positive for herpes simplex 1 virus. instead was preserved in the anterior abdominal wall.
Anti-cerebral edema medications were tapered and
Cerebrospinal fluid meningoencephalitis profile stopped postoperatively.
[Table 1] is a polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
equivalent. This is a molecular diagnostic screening Postoperatively, his neurological status stabilized and
technology involving isolation of the genetic material was weaned off ventilator gradually. Postoperative
of the causative agent from the given specimen and
computed tomography (CT) of brain [Figure 2] after
3 days showed resolution of the mass effect with
Table 1: CSF study no midline shift. However, the right temporal lobe
Parameters Results remained hypodense. Basal ganglia, thalamus, internal
CSF protein 60 mg/dL capsule, and caudate nucleus appeared normal.
CSF sugar 87 mg/dL
CSF cells 200 cells/mm with predominantly
3
polymorphs (P64, L28) Electroencephalography (EEG) in the postoperative
CSF meningo‑ Positive for herpes simplex‑1 period showed diffuse right hemispherical slowing in
encephalitic profile theta to delta range [Figure 3]. Histopathology of the
CSF: cerebrospinal fluid
right temporal lesion [Table 2] revealed infiltration
a b
Figure 1: Magnetic resonance imaging of brain: T2‑weighted sequence showing
swollen and edematous right temporal lobe (a) with mass effect (b) and midline Figure 2: Postoperative computed tomography of brain after 3 days showing
shift as indicated by the arrow resolution of the mass effect with no midline shift
182 Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation | Volume 2 | Issue 3 | July 15, 2015 Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation | Volume 2 | Issue 3 | July 15, 2015 183