Page 132 - Read Online
P. 132
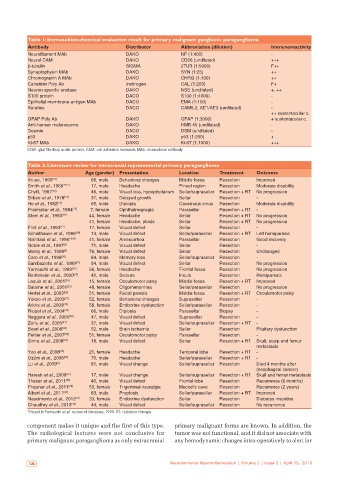
Table 1: Immunohistochemical evaluation result for primary malignant ganglionic paraganglioma
Antibody Distributor Abbreviation (dilution) Immunoreactivity
Neurofilament MAb DAKO NF (1:400) -
Neural CAM DAKO CD56 (undiluted) +++
β-tubulin SIGMA βTUB (1:5000) F++
Synaptophysin MAb DAKO SYN (1:25) ++
Chromogranin A MAb DAKO CHRG (1:100) ++
Calretinin Poly Ab Invitrogen CAL (1:200) F+
Neuron‑specific enolase DAKO NSE (undiluted) +, ++
S100 protein DACO S100 (1:4000) -
Epithelial membrane antigen MAb DACO EMA (1:100) -
Keratins DACO CAM5.2, AE1/AE3 (undiluted) -
++ sustentacular c.
GFAP Poly Ab DAKO GFAP (1:3000) + sustentacular c.
Anti-human melanosome DAKO HMB 45 (undiluted) -
Desmin DACO DSM (undiluted) -
p53 DAKO p53 (1:200) +
Ki-67 MAb DAKO Ki-67 (1:1000) +++
GFAP: glial fibrillary acidic protein; CAM: cell adhesion molecule; MAb: monoclonal antibody
Table 2: Literature review for intracranial supratentorial primary paraganglioma
Author Age (gender) Presentation Location Treatment Outcome
Kruse, 1960 [10] 68, male Behavioral changes Middle fossa Resection Improved
Smith et al., 1966* [11] 17, male Headache Pineal region Resection Moderate disability
Chytil, 1967 [12] 46, male Visual loss, hypopituitarism Sellar/suprasellar Resection + RT No progression
Bilbao et al., 1978 [13] 37, male Delayed growth Sellar Resection -
Ho et al., 1982 [14] 65, male Diplopia Cavernous sinus Resection Moderate disability
Prabhakar et al., 1984 [15] 7, female Ophthalmoplegia Parasellar Resection + RT -
Steel et al., 1993 [16] 44, female Headache Sellar Resection + RT No progression
41, female Headache, ptosis Sellar Resection + RT No progression
Flint et al., 1993 [17] 17, female Visual defect Sellar Resection -
Scheithauer et al., 1996 [18] 14, male Visual defect Sellar/parasellar Resection + RT Left hemiparesis
Nishitani et al., 1996* [19] 41, female Amenorrhea Parasellar Resection Good recovery
Noble et al., 1997 [8] 71, male Visual defect Sellar Resection -
Mokry et al., 1998 [9] 76, female Visual defect Sellar Resection Unchanged
Caro et al., 1998 [20] 84, male Memory loss Sellar/suprasellar Resection -
Sambaziotis et al., 1999 [21] 54, male Visual defect Sellar Resection No progression
Yamauchi et al., 1999 [22] 56, female Headache Frontal fossa Resection No progression
Reithmeier et al., 2000 [23] 42, male Seizure Insula Resection Hemiparesis
Laquis et al., 2001 [24] 15, female Occulomotor palsy Middle fossa Resection + RT Improved
Salame et al., 2001 [25] 48, female Oligomenorrhea Sellar/parasellar Resection No progression
Hertel et al., 2003 [26] 51, female Facial paresis Middle fossa Resection + RT Occulomotor palsy
Yokoo et al., 2003 [27] 52, female Behavioral changes Suprasellar Resection -
Arkha et al., 2003 [28] 58, female Endocrine dysfunction Sellar/parasellar Resection -
Riopel et al., 2004 [29] 66, male Diplopia Parasellar Biopsy -
Naggara et al., 2005 [30] 47, male Visual defect Suprasellar Resection -
Zorlu et al., 2005 [31] 37, male Visual defect Sellar/suprasellar Resection + RT -
Boari et al., 2006 [32] 52, male Brain ischemia Sellar Resection Pituitary dysfunction
Peltier et al., 2007 [33] 51, female Occulomotor palsy Parasellar Resection -
Sinha et al., 2008 [34] 18, male Visual defect Sellar Resection + RT Skull, scalp and femur
metastasis
Yoo et al., 2008 [35] 21, female Headache Temporal lobe Resection + RT -
Ozüm et al., 2008 [36] 70, male Headache Sellar/parasellar Resection + RT -
Lu et al., 2009 [5] 81, male Visual change Sellar/suprasellar Resection Died 4 months after
(esophageal cancer)
Haresh et al., 2009 [37] 17, male Visual change Sellar/suprasellar Resection + RT Skull and femur metastasis
Thakar et al., 2011 [38] 40, male Visual defect Frontal lobe Resection Recurrence (6 months)
Prajsnar et al., 2011 [39] 53, female Trigeminal neuralgia Meckel’s cave Resection Recurrence (2 years)
Albert et al., 2011 [40] 63, male Proptosis Sellar/parasellar Resection + RT Improved
Nascimento et al., 2012 [41] 33, female Endocrine dysfunction Sellar Resection Diabetes insipidus
Chaudhry et al., 2013 [42] 44, male Visual defect Sellar/suprasellar Resection No recurrence
*Found in Yamauchi et al. review of literature, 1999. RT: radiation therapy
component makes it unique and the first of this type. primary malignant forms are known. In addition, the
The radiological features were not conclusive for tumor was not functional, and it did not associate with
primary malignant paraganglioma as only extracranial any hemodynamic changes intra-operatively to alert for
124 Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation | Volume 2 | Issue 2 | April 15, 2015