Page 97 - Read Online
P. 97
A detailed history revealed past history of arthralgias 4 limbs. Follow-up MRI [Figure 5] showed significant
and photosensitivity, for which she was not on any resolution of white matter edema. Hence, on the basis
treatment. On clinical examination, she was in grade 3 of arthralgias and photosensitivity in past and features
encephalopathy with Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) of polyserositis, renal impairment and neurological
of 8/15, hemodynamically stable, with generalized dysfunction in the form of encephalopathy, a
areflexia. Rest of the systemic examination was normal. likely diagnosis of seronegative systemic lupus
Serum urea and creatinine levels were on higher erythematosus (SLE) presenting first time as PRES,
side (serum urea = 88, serum creatinine = 1.9), whereas was established. Patient is presently on oral tapering
rest of the baseline investigation and biochemistry dose of steroids along with supportive treatment.
were within the normal limits. Ultrasound abdomen
showed bilateral raised cortical echogenicity, with DISCUSSION
mild ascites. Repeat vasculitic profile including ANA,
anti-ds-DNA, Perinuclear anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic The exact pathophysiological mechanism of PRES
antibodies (P-ANCA), cytoplasmic antineutrophil remains uncertain. To date, three hypotheses have been
cytoplasmic antibodies (C-ANCA), anticentromere proposed, which include: (1) cerebral vasoconstriction
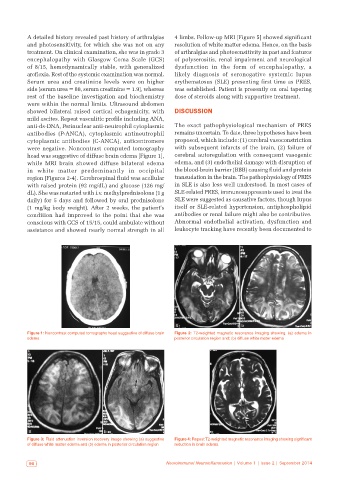
were negative. Noncontrast computed tomography with subsequent infarcts of the brain, (2) failure of
head was suggestive of diffuse brain edema [Figure 1], cerebral autoregulation with consequent vasogenic
while MRI brain showed diffuse bilateral edema edema, and (3) endothelial damage with disruption of
in white matter predominantly in occipital the blood-brain barrier (BBB) causing fluid and protein
region [Figures 2-4]. Cerebrospinal fluid was acellular transudation in the brain. The pathophysiology of PRES
with raised protein (92 mg/dL) and glucose (126 mg/ in SLE is also less well understood. In most cases of
dL). She was restarted with i.v. methylprednisolone (1 g SLE-related PRES, immunosuppresants used to treat the
daily) for 5 days and followed by oral prednisolone SLE were suggested as causative factors, though lupus
(1 mg/kg body weight). After 2 weeks, the patient’s itself or SLE-related hypertension, antiphospholipid
condition had improved to the point that she was antibodies or renal failure might also be contributive.
conscious with GCS of 15/15, could ambulate without Abnormal endothelial activation, dysfunction and
assistance and showed nearly normal strength in all leukocyte tracking have recently been documented to
a b
Figure 1: Noncontrast computed tomography head suggestive of diffuse brain Figure 2: T2‑weighted magnetic resonance imaging showing. (a) edema in
edema posterior circulation region and; (b) diffuse white mater edema
a b
Figure 3: Fluid attenuation inversion recovery image showing (a) suggestive Figure 4: Repeat T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging showing significant
of diffuse white matter edema and (b) edema in posterior circulation region reduction in brain edema
90 Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation | Volume 1 | Issue 2 | September 2014