Page 39 - Read Online
P. 39
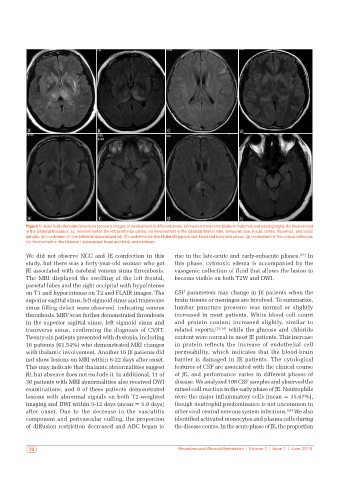
a b c d
e f g h
Figure 1: Axial fluid attenuated inversion recovery images of involvement in different areas: (a) Involvement in the bilateral thalamus and basal ganglia; (b) Involvement
in the bilateral thalamus; (c) Involvement in the left prefrontal cortex; (d) Involvement in the bilateral frontal lobe, temporal lobe, insula cortex, thalamus, and basal
ganglia; (e) Involvement in the bilateral hippocampal tail; (f) Involvement in the bilateral hippocampal head and body and uncus; (g) Involvement in the corpus callosum;
(h) Involvement in the bilateral hippocampal head and body and midbrain
We did not observe NCC and JE coinfection in this rise in the late-acute and early-subacute phases. [17] In
study, but there was a forty-year-old woman who got this phase, cytotoxic edema is accompanied by the
JE associated with cerebral venous sinus thrombosis. vasogenic collection of fluid that allows the lesion to
The MRI displayed the swelling of the left frontal, become visible on both T2W and DWI.
parietal lobes and the right occipital with hypointense
on T1 and hyperintense on T2 and FLAIR images. The CSF parameters may change in JE patients when the
superior sagittal sinus, left sigmoid sinus and transverse brain tissues or meninges are involved. To summarize,
sinus filling defect were observed, indicating venous lumbar puncture pressure was normal or slightly
thrombosis. MRV scan further demonstrated thrombosis increased in most patients. White blood cell count
in the superior sagittal sinus, left sigmoid sinus and and protein content increased slightly, similar to
transverse sinus, confirming the diagnosis of CVST. related reports, [23,24] while the glucose and chloride
Twenty-six patients presented with dystonia, including content were normal in most JE patients. This increase
16 patients (61.54%) who demonstrated MRI changes in protein reflects the increase of endothelial cell
with thalamic involvement. Another 16 JE patients did permeability, which indicates that the blood-brain
not show lesions on MRI within 6-22 days after onset. barrier is damaged in JE patients. The cytological
This may indicate that thalamic abnormalities suggest features of CSF are associated with the clinical course
JE, but absence does not exclude it. In additional, 11 of of JE, and performance varies in different phases of
30 patients with MRI abnormalities also received DWI disease. We analyzed 108 CSF samples and observed the
examinations, and 9 of these patients demonstrated mixed-cell reaction in the early phase of JE. Neutrophils
lesions with abnormal signals on both T2-weighted were the major inflammatory cells (mean = 35.67%),
imaging and DWI within 5-12 days (mean = 5.9 days) though neutrophil predominance is not uncommon in
after onset. Due to the decrease in the vasculitis other viral central nervous system infections. [25] We also
component and perivascular cuffing, the proportion identified activated monocytes and plasma cells during
of diffusion restriction decreased and ADC began to the disease course. In the acute phase of JE, the proportion
32 Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation | Volume 1 | Issue 1 | June 2014