Page 139 - Read Online
P. 139
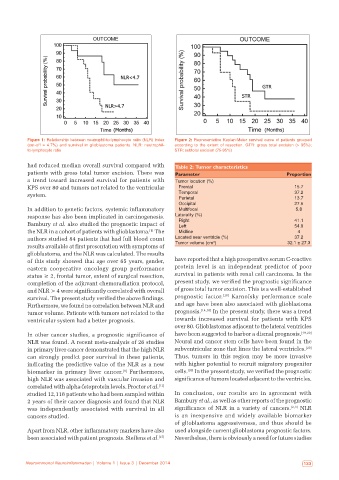
Figure 1: Relationship between neutrophil‑to‑lymphocyte ratio (NLR) index Figure 2: Representative Kaplan‑Meier survival curve of patients grouped
(cut‑off = 4.7%) and survival in glioblastoma patients. NLR: neutrophil‑ according to the extent of resection. GTR: gross total excision (> 95%);
to‑lymphocyte ratio STR: subtotal excision (75‑95%)
had reduced median overall survival compared with Table 2: Tumor characteristics
patients with gross total tumor excision. There was Parameter Proportion
a trend toward increased survival for patients with Tumor location (%)
KPS over 80 and tumors not related to the ventricular Frontal 15.7
system. Temporal 37.2
Parietal 13.7
Occipital 27.5
In addition to genetic factors, systemic inflammatory Multifocal 5.8
response has also been implicated in carcinogenesis. Laterality (%)
Bambury et al. also studied the prognostic impact of Right 41.1
54.9
Left
the NLR in a cohort of patients with glioblastoma. The Midline 4
[1]
authors studied 84 patients that had full blood count Located near ventricle (%) 37.2
3
results available at first presentation with symptoms of Tumor volume (cm ) 32.1 ± 27.3
glioblastoma, and the NLR was calculated. The results
of this study showed that age over 65 years, gender, have reported that a high preoperative serum C‑reactive
eastern cooperative oncology group performance protein level is an independent predictor of poor
status ≥ 2, frontal tumor, extent of surgical resection, survival in patients with renal cell carcinoma. In the
completion of the adjuvant chemoradiation protocol, present study, we verified the prognostic significance
and NLR > 4 were significantly correlated with overall of gross total tumor excision. This is a well‑established
survival. The present study verified the above findings. prognostic factor. [18] Karnofsky performance scale
Furthermore, we found no correlation between NLR and and age have been also associated with glioblastoma
tumor volume. Patients with tumors not related to the prognosis. [14,18] In the present study, there was a trend
ventricular system had a better prognosis. towards increased survival for patients with KPS
over 80. Glioblastomas adjacent to the lateral ventricles
In other cancer studies, a prognostic significance of have been suggested to harbor a dismal prognosis. [19,20]
NLR was found. A recent meta‑analysis of 26 studies Neural and cancer stem cells have been found in the
in primary liver cancer demonstrated that the high NLR subventricular zone that lines the lateral ventricles. [20]
can strongly predict poor survival in these patients, Thus, tumors in this region may be more invasive
indicating the predictive value of the NLR as a new with higher potential to recruit migratory progenitor
[6]
biomarker in primary liver cancer. Furthermore, cells. [20] In the present study, we verified the prognostic
high NLR was associated with vascular invasion and significance of tumors located adjacent to the ventricles.
[12]
correlated with alpha‑fetoprotein levels. Proctor et al.
studied 12,118 patients who had been sampled within In conclusion, our results are in agreement with
2 years of their cancer diagnosis and found that NLR Bambury et al., as well as other reports of the prognostic
was independently associated with survival in all significance of NLR in a variety of cancers. [2,3] NLR
cancers studied. is an inexpensive and widely available biomarker
of glioblastoma aggressiveness, and thus should be
Apart from NLR, other inflammatory markers have also used alongside current glioblastoma prognostic factors.
been associated with patient prognosis. Steffens et al. Nevertheless, there is obviously a need for future studies
[17]
Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation | Volume 1 | Issue 3 | December 2014 133