Page 138 - Read Online
P. 138
for up to 1‑year or until recurrence. Radiotherapy was met the inclusion criteria for the study. The majority of
administered as fractionated focal irradiation at a dose glioblastomas were lateralized, with 28 (54.9%) on the
of 2 Gy/fraction given once a day for 5 days/week left and 21 (41.1%) on the right side. The most common
over a period of 6 weeks up to a total dose of 60 Gy. tumor site was the temporal lobe (37.2%), followed by
Follow‑up MRIs were performed every 2 months. the occipital lobe (27.5%). The mean tumor volume
Recurrence was defined based on MRI and/or single was 32.1 ± 27.3 cm . In 19 cases (37.2%), the tumor
3
photon emission tomography findings. [16] The study was located close to a ventricle. Thirty‑four patients
was approved by the Institutional Review Board. had a KPS over 80. In 32 cases, gross total excision was
achieved, whereas in 19 cases there was subtotal tumor
Statistical analysis resection. One patient was lost to follow‑up, and one
Pearson’s correlation coefficient was used to assess patient died in the immediate postoperative period.
continuous variables. Progression‑free survival (PFS) After a mean follow‑up period of 17 months (range:
was defined as the time from the initial surgery to 3‑39 months), 14 patients were alive.
demonstration of tumor progression on follow‑up MRI
or to death. Survival time was defined as the time Neutrophil‑to‑lymphocyte ratio
between the date of diagnosis and the date of death for The mean NLR was 6.7 ± 4.6. Using ROC curve analysis,
deceased patients, or to the last follow‑up for surviving a cut‑off NLR value of 4.7 was determined to best
patients. The overall survival time was estimated using predict survival. Patients with an NLR exceeding 4.7
Kaplan‑Meier methods, and log‑rank analysis was differed significantly from those with an NLR ≤ 4.7 and
performed to compare survival curves between groups. were associated with decreased survival time (11 vs.
Patients who were still alive at last contact were treated 18.7 months, P = 0.01) [Figure 1]. There was a significant
as censored events in the analysis. Multivariate Cox increase in PFS for patients with an NLR lower than
regression analysis of the data was used to analyze 4.73 (P = 0.03).
possible prognostic factors. The forward step‑wise model
selection procedure was used (P value of likelihood‑ratio Extent of resection
test < 0.05 as inclusion criteria; likelihood‑ratio test Patients with gross total tumor excision had a
> 0.10 as exclusion criteria) to define the final model. median survival of 18 months, whereas in patients
The following variables were entered: gender, age at with subtotal tumor excision, the median survival
diagnosis, KPS, NLR, and the extent of resection. With time was 11 months. The difference was statistically
respect to NLR, receiving operating characteristics (ROC) significant (P = 0.036) [Figure 2].
curve analysis was performed in order to determine the
cut‑off value for predicting survival. A 2‑sided P < 0.05 Karnofsky performance status score
was considered as statistically significant. The median survival for patients with KPS over 80
was 17 months, whereas survival for patients with
RESULTS KPS under or equal to 80 was 11 months. However,
the difference was marginally significant (P = 0.052).
Study population No significant difference in survival was observed with
Table 1 summarizes the patient data. Fifty‑one respect to patient age (P = 0.4) or gender (P = 0.3).
patients (30 males, 21 females, mean age 59.2 ± 14.2)
Tumor characteristics
In 19 cases, the tumor was located close to a ventricle.
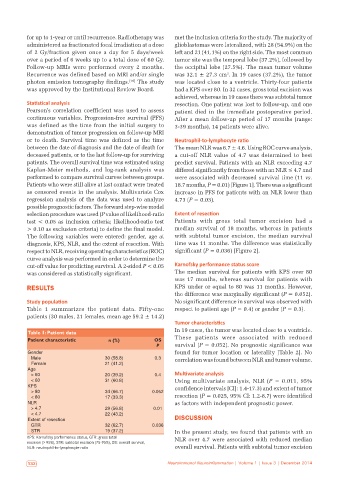
Table 1: Patient data
Patient characteristic n (%) OS These patients were associated with reduced
P survival (P = 0.052). No prognostic significance was
Gender found for tumor location or laterality [Table 2]. No
Male 30 (58.8) 0.3 correlation was found between NLR and tumor volume.
Female 21 (41.2)
Age
> 60 20 (39.2) 0.4 Multivariate analysis
< 60 31 (60.8) Using multivariate analysis, NLR (P = 0.011, 95%
KPS confidence intervals [CI]: 1.4‑17.3) and extent of tumor
> 80 34 (66.7) 0.052
< 80 17 (33.3) resection (P = 0.025, 95% CI: 1.2‑8.7) were identified
NLR as factors with independent prognostic power.
> 4.7 29 (56.8) 0.01
< 4.7 22 (43.2)
Extent of resection DISCUSSION
GTR 32 (62.7) 0.036
STR 19 (37.2) In the present study, we found that patients with an
KPS: Karnofsky performance status, GTR: gross total NLR over 4.7 were associated with reduced median
excision (> 95%), STR: subtotal excision (75-95%), OS: overall survival,
NLR: neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio overall survival. Patients with subtotal tumor excision
132 Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation | Volume 1 | Issue 3 | December 2014