Page 134 - Read Online
P. 134
and males in Australia are 27.9 and 21.9/1 million, and ryanodine receptor are detected in about 50% of
respectively, with a female predominance. A similar such patients. [23] Thymoma‑associated MG involves
[6]
tendency was shown in Taiwan where the incidence MG patients with thymoma regardless of the extent of
ratio of males to females is 0.68. However, three muscular involvement, accounting for about 10‑15% of
[8]
studies with large sample sizes showed a nearly equal all MG patients. Male and female patients are equally
incidence for both sexes in mainland China. [13‑15] common in this subtype, and MG occurs at any age
Considering age and sex, the occurrence of MG exhibits with a peak onset age of 50 years. [28,29] In seronegative
a bimodal fashion. Below 40 years of age, the ratio of MG patients, anti‑AChR and anti‑MuSK antibodies are
female to male is nearly 3:1; however, during puberty undetectable. Clinical features such as variable age of
and between 40 and 50 years, the incidence rate is onset, lack of thymoma and variable extent and severity
[30]
roughly equal. Over 50 years, MG is more common in of muscular involvement are also found. The detailed
males, with a ratio of 3:2. [16] Osserman and Genkins characteristics of all subtypes are listed in Table 2.
have observed two peaks of incidence in MG, with
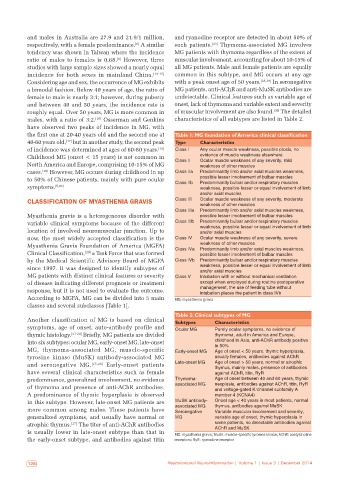
the first one at 20‑40 years old and the second one at Table 1: MG foundation of America clinical classification
40‑60 years old, but in another study, the second peak Type Characteristics
[17]
of incidence was determined at ages of 60‑80 years. [18] Class I Any ocular muscle weakness, possible ptosis, no
Childhood MG (onset < 15 years) is not common in evidence of muscle weakness elsewhere
North America and Europe, comprising 10‑15% of MG Class II Ocular muscle weakness of any severity, mild
weakness of other muscles
cases. [19] However, MG occurs during childhood in up Class IIa Predominantly limb and/or axial muscles weakness,
to 50% of Chinese patients, mainly with pure ocular Class IIb possible lesser involvement of bulbar muscles
Predominantly bulbar and/or respiratory muscles
symptoms. [5,13] weakness, possible lesser or equal involvement of limb
and/or axial muscles
CLASSIFICATION OF MYASTHENIA GRAVIS Class III Ocular muscle weakness of any severity, moderate
weakness of other muscles
Class IIIa Predominantly limb and/or axial muscles weakness,
Myasthenia gravis is a heterogeneous disorder with possible lesser involvement of bulbar muscles
variable clinical symptoms because of the different Class IIIb Predominantly bulbar and/or respiratory muscles
location of involved neuromuscular junction. Up to weakness, possible lesser or equal involvement of limb
and/or axial muscles
now, the most widely accepted classification is the Class IV Ocular muscle weakness of any severity, severe
Myasthenia Gravis Foundation of America (MGFA) weakness of other muscles
Clinical Classification, [20] a Task Force that was formed Class IVa Predominantly limb and/or axial muscles weakness,
possible lesser involvement of bulbar muscles
by the Medical Scientific Advisory Board of MGFA Class IVb Predominantly bulbar and/or respiratory muscles
since 1997. It was designed to identify subtypes of weakness, possible lesser or equal involvement of limb
and/or axial muscles
MG patients with distinct clinical features or severity Class V Intubation with or without mechanical ventilation
of disease indicating different prognosis or treatment except when employed during routine postoperative
response, but it is not used to evaluate the outcome. management, the use of feeding tube without
intubation places the patient in class IVb
According to MGFA, MG can be divided into 5 main MG: myasthenia gravis
classes and several subclasses [Table 1].
Table 2: Clinical subtypes of MG
Another classification of MG is based on clinical Subtypes Characteristics
symptoms, age of onset, auto‑antibody profile and Ocular MG Purely ocular symptoms, no evidence of
thymic histology. [21‑24] Briefly, MG patients are divided thymoma, adult in America and Europe,
into six subtypes: ocular MG, early‑onset MG, late‑onset childhood in Asia, anti‑AChR antibody positive
in 50%
MG, thymoma‑associated MG, muscle‑specific Early‑onset MG Age of onset < 50 years, thymic hyperplasia,
tyrosine kinase (MuSK) antibody‑associated MG usually females, antibodies against AChR
and seronegative MG. [25,26] Early‑onset patients Late‑onset MG Age of onset > 50 years, normal or atrophic
thymus, mainly males, presence of antibodies
have several clinical characteristics such as female against AChR, titin, RyR
predominance, generalized involvement, no evidence Thymoma‑ Age of onset between 40 and 60 years, thymic
of thymoma and presence of anti‑AChR antibodies. associated MG neoplasia, antibodies against AChR, titin, RyR
and voltage‑gated K channel subfamily A
+
A predominance of thymic hyperplasia is observed member 4 (KCNA4)
in this subtype. However, late‑onset MG patients are MuSK antibody‑ Onset age < 40 years in most patients, normal
more common among males. These patients have associated MG thymus, antibodies against MuSK
Variable muscular involvement and severity,
Seronegative
generalized symptoms, and usually have normal or MG variable age of onset, thymic hyperplasia in
atrophic thymus. [27] The titer of anti‑AChR antibodies some patients, no detectable antibodies against
AChR and MuSK
is usually lower in late‑onset subtype than that in MG: myasthenia gravis; MuSK: muscle‑specific tyrosine kinase; AChR: acetylcholine
the early‑onset subtype, and antibodies against titin receptors; RyR: ryanodine receptor
128 Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation | Volume 1 | Issue 3 | December 2014