Page 574 - Read Online
P. 574
Page 6 of 15 Cossu et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2020;4:60 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2020.52
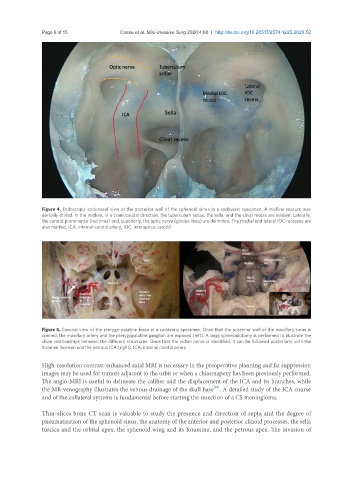
Figure 4. Endoscopic endonasal view of the posterior wall of the sphenoid sinus in a cadaveric specimen. A midline septum was
partially drilled. In the midline, in a craniocaudal direction, the tuberculum sellae, the sella, and the clival recess are evident. Laterally,
the carotid prominence (red lines) and, superiorly, the optic nerve (golden lines) are delimited. The medial and lateral IOC recesses are
also marked. ICA: internal carotid artery; IOC: interoptico-carotid
Figure 5. Coronal view of the pterygo-palatine fossa in a cadaveric specimen. Once that the posterior wall of the maxillary sinus is
opened, the maxillary artery and the pterygopalatine ganglion are exposed (left). A large sphenoidotomy is performed to illustrate the
close relationships between the different structures. Once that the vidian nerve is identified, it can be followed posteriorly until the
foramen lacerum and the petrous ICA (right). ICA: internal carotid artery
High-resolution contrast-enhanced axial MRI is necessary in the preoperative planning and fat suppression
images may be used for tumors adjacent to the orbit or when a chiasmapexy has been previously performed.
The angio-MRI is useful to delineate the caliber and the displacement of the ICA and its branches, while
[26]
the MR-venography illustrates the venous drainage of the skull base . A detailed study of the ICA course
and of the collateral systems is fundamental before starting the resection of a CS meningioma.
Thin-slices bone CT scan is valuable to study the presence and direction of septa and the degree of
pneumatization of the sphenoid sinus, the anatomy of the anterior and posterior clinoid processes, the sella
turcica and the orbital apex, the sphenoid wing and its foramina, and the petrous apex. The invasion of