Page 92 - Read Online
P. 92
Ackerman et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2021;5:14 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2021.02 Page 11 of 19
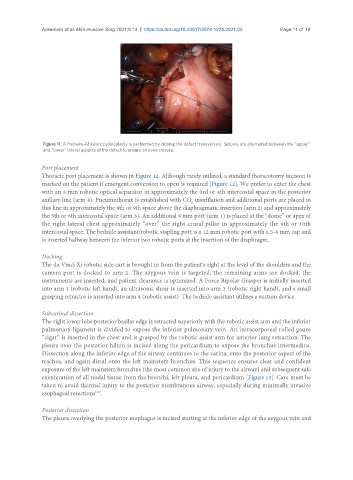
Figure 11. A Heineke-Mikulicz pyloroplasty is performed by closing the defect transversely. Sutures are alternated between the “upper”
and “lower” lateral aspects of the defect to ensure an even closure.
Port placement
Thoracic port placement is shown in Figure 12. Although rarely utilized, a standard thoracotomy incision is
marked on the patient if emergent conversion to open is required [Figure 12]. We prefer to enter the chest
with an 8 mm robotic optical separator in approximately the 3rd or 4th intercostal space in the posterior
axillary line (arm 4). Pneumothorax is established with CO insufflation and additional ports are placed in
2
this line in approximately the 8th or 9th space above the diaphragmatic insertion (arm 2) and approximately
the 5th or 6th intercostal space (arm 3). An additional 8 mm port (arm 1) is placed at the “dome” or apex of
the right lateral chest approximately “over” the right crural pillar in approximately the 9th or 10th
intercostal space. The bedside assistant/robotic stapling port is a 12 mm robotic port with a 5-8 mm cap and
is inserted halfway between the inferior two robotic ports at the insertion of the diaphragm.
Docking
The da Vinci Xi robotic side cart is brought in from the patient’s right at the level of the shoulders and the
camera port is docked to arm 2. The azygous vein is targeted, the remaining arms are docked, the
instruments are inserted, and patient clearance is optimized. A Force Bipolar Grasper is initially inserted
into arm 1 (robotic left hand), an ultrasonic shear is inserted into arm 3 (robotic right hand), and a small
grasping retractor is inserted into arm 4 (robotic assist). The bedside assistant utilizes a suction device.
Subcarinal dissection
The right lower lobe posterior basilar edge is retracted superiorly with the robotic assist arm and the inferior
pulmonary ligament is divided to expose the inferior pulmonary vein. An intracorporeal rolled gauze
“cigar” is inserted in the chest and is grasped by the robotic assist arm for anterior lung retraction. The
pleura over the posterior hilum is incised along the pericardium to expose the bronchus intermedius.
Dissection along the inferior edge of the airway continues to the carina, onto the posterior aspect of the
trachea, and again distal onto the left mainstem bronchus. This sequence ensures clear and confident
exposure of the left mainstem bronchus (the most common site of injury to the airway) and subsequent safe
exenteration of all nodal tissue from the bronchi, left pleura, and pericardium [Figure 13]. Care must be
taken to avoid thermal injury to the posterior membranous airway, especially during minimally invasive
esophageal resections .
[29]
Posterior dissection
The pleura overlying the posterior esophagus is incised starting at the inferior edge of the azygous vein and