Page 80 - Read Online
P. 80
Page 10 of 15 Tropiano et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2024;8:17 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2024.41
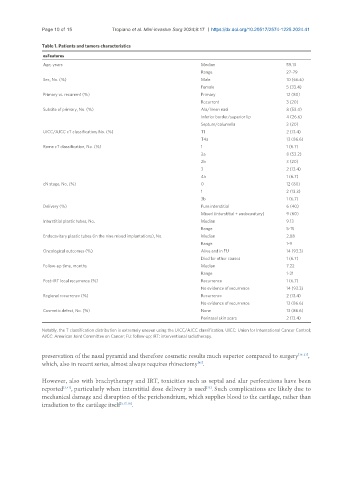
Table 1. Patients and tumors characteristics
esFeatures
Age, years Median 59.13
Range 27-79
Sex, No. (%) Male 10 (66.6)
Female 5 (33.4)
Primary vs. recurrent (%) Primary 12 (80)
Recurrent 3 (20)
Subsite of primary, No. (%) Ala/limen nasi 8 (53.4)
Inferior border/superior lip 4 (26.6)
Septum/columella 3 (20)
UICC/AJCC cT classification, No. (%) T1 2 (13.4)
T4a 13 (86.6)
Rome cT classification, No. (%) 1 1 (6.7)
2a 8 (53.2)
2b 3 (20)
3 2 (13.4)
4a 1 (6.7)
cN stage, No. (%) 0 12 (80)
1 2 (13.3)
3b 1 (6.7)
Delivery (%) Pure interstitial 6 (40)
Mixed (interstitial + endocavitary) 9 (60)
Interstitial plastic tubes, No. Median 9.13
Range 5-15
Endocavitary plastic tubes (in the nine mixed implantations), No. Median 2.88
Range 1-9
Oncological outcomes (%) Alive and in FU 14 (93.3)
Died for other causes 1 (6.7)
Follow-up time, months Median 7.22
Range 1-21
Post-IRT local recurrence (%) Recurrence 1 (6.7)
No evidence of recurrence 14 (93.3)
Regional recurrence (%) Recurrence 2 (13.4)
No evidence of recurrence 13 (86.6)
Cosmetic defect, No. (%) None 13 (86.6)
Perinasal skin scars 2 (13.4)
Notably, the T classification distribution is extremely uneven using the UICC/AJCC classification. UICC: Union for International Cancer Control;
AJCC: American Joint Committee on Cancer; FU: follow-up; IRT: interventional radiotherapy.
preservation of the nasal pyramid and therefore cosmetic results much superior compared to surgery [16-21] ,
[45]
which, also in recent series, almost always requires rhinectomy .
However, also with brachytherapy and IRT, toxicities such as septal and alar perforations have been
[23]
reported [3,41] , particularly when interstitial dose delivery is used . Such complications are likely due to
mechanical damage and disruption of the perichondrium, which supplies blood to the cartilage, rather than
irradiation to the cartilage itself [3,17,18] .