Page 53 - Read Online
P. 53
Kitahama et al. PLPED with EMG monitoring under general anesthesia
[20]
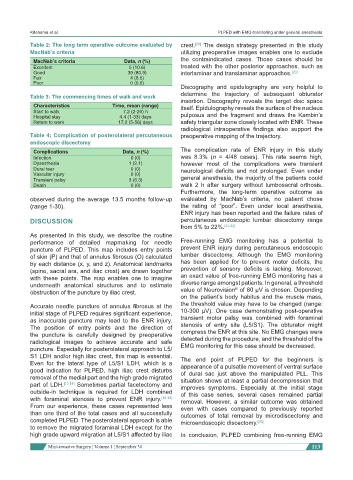
Table 2: The long term operative outcome evaluated by crest. The design strategy presented in this study
MacNab’s criteria utilizing preoperative images enables one to exclude
MacNab’s criteria Data, n (%) the contraindicated cases. Those cases should be
Excellent 5 (10.6) treated with the other posterior approaches, such as
Good 39 (80.9) interlaminar and translaminar approaches. [20]
Fair 4 (8.5)
Poor 0 (0.0)
Discography and epidulography are very helpful to
determine the trajectory of subsequent obturator
Table 3: The commencing times of walk and work
insertion. Discography reveals the target disc space
Characteristics Time, mean (range) itself. Epidulography reveals the surface of the nucleus
Start to walk 7.2 (2-20) h
Hospital stay 4.4 (1-33) days pulposus and the fragment and draws the Kambin’s
Return to work 17.2 (5-56) days safety triangular zone closely located with ENR. These
radiological intraoperative findings also support the
Table 4: Complication of posterolateral percutaneous preoperative mapping of the trajectory.
endoscopic discectomy
Complications Data, n (%) The complication rate of ENR injury in this study
Infection 0 (0) was 8.3% (n = 4/48 cases). This rate seems high,
Dysesthesia 1 (2.1) however most of the complications were transient
Dural tear 0 (0) neurological deficits and not prolonged. Even under
Vascular injury 0 (0)
Transient palsy 3 (6.3) general anesthesia, the majority of the patients could
Death 0 (0) walk 2 h after surgery without lumbosacral orthosis.
Furthermore, the long-term operative outcome as
observed during the average 13.5 months follow-up evaluated by MacNab’s criteria, no patient chose
(range 1-30). the rating of “poor”. Even under local anesthesia,
ENR injury has been reported and the failure rates of
DISCUSSION percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy range
from 5% to 22%. [21-24]
As presented in this study, we describe the routine
performance of detailed mapmaking for needle Free-running EMG monitoring has a potential to
puncture of PLPED. This map includes entry points prevent ENR injury during percutaneous endoscopic
of skin (P) and that of annulus fibrosus (O) calculated lumbar discectomy. Although the EMG monitoring
by each distance (x, y, and z). Anatomical landmarks has been applied for to prevent motor deficits, the
(spine, sacral ara, and iliac crest) are drawn together prevention of sensory deficits is lacking. Moreover,
with these points. The map enables one to imagine an exact value of free-running EMG monitoring has a
underneath anatomical structures and to estimate diverse range amongst patients. In general, a threshold
®
obstruction of the puncture by iliac crest. value of Neurovision of 80 μV is chosen. Depending
on the patient’s body habitus and the muscle mass,
Accurate needle puncture of annulus fibrosus at the the threshold value may have to be changed (range:
initial stage of PLPED requires significant experience, 10-300 μV). One case demonstrating post-operative
as inaccurate puncture may lead to the ENR injury. transient motor palsy was combined with foraminal
The position of entry points and the direction of stenosis of entry site (L5/S1). The obturator might
the puncture is carefully designed by preoperative compress the ENR at this site. No EMG changes were
radiological images to achieve accurate and safe detected during the procedure, and the threshold of the
EMG monitoring for this case should be decreased.
puncture. Especially for posterolateral approach to L5/
S1 LDH and/or high iliac crest, this map is essential. The end point of PLPED for the beginners is
Even for the lateral type of L5/S1 LDH, which is a appearance of a pulsatile movement of ventral surface
good indication for PLPED, high iliac crest disturbs of dural sac just above the manipulated PLL. This
removal of the medial part and the high grade migrated situation shows at least a partial decompression that
part of LDH. [13,14] Sometimes partial facetectomy and improves symptoms. Especially at the initial stage
outside-in technique is required for LDH combined of this case series, several cases remained partial
with foraminal stenosis to prevent ENR injury. [15-19] removal. However, a similar outcome was obtained
From our experience, these cases represented less even with cases compared to previously reported
than one third of the total cases and all successfully outcomes of total removal by microdiscectomy and
completed PLPED. The posterolateral approach is able microendoscopic discectomy. [25]
to remove the migrated foraminal LDH except for the
high grade upward migration at L5/S1 affected by iliac In conclusion, PLPED combining free-running EMG
Mini-invasive Surgery ¦ Volume 1 ¦ September 30 113