Page 12 - Read Online
P. 12
Bhardwaj MicroRNAs in atopic dermatitis
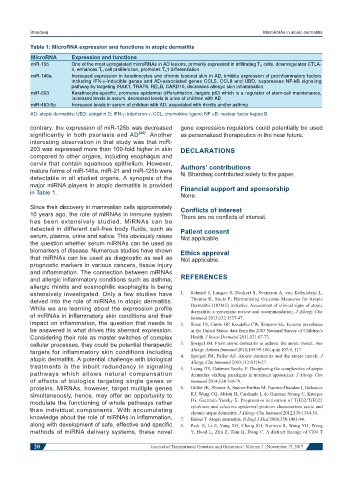
Table 1: MicroRNA expression and functions in atopic dermatitis
MicroRNA Expression and functions
miR-155 One of the most upregulated microRNAs in AD lesions, primarily expressed in infiltrating T H cells, downregulates CTLA-
4, enhances T H cell proliferation, promotes T H 1 differentiation
miR-146a Increased expression in keratinocytes and chronic lesional skin in AD, inhibits expression of proinflammatory factors
including IFN-g-inducible genes and AD-associated genes CCL5, CCL8 and UBD, suppresses NF-kB signaling
pathway by targeting IRAK1, TRAF6, RELB, CARD10, decreases allergic skin inflammation
miR-203 Keratinocyte-specific, promotes epidermal differentiation, targets p63 which is a regulator of stem-cell maintenance,
increased levels in serum, decreased levels in urine of children with AD
miR-483-5p Increased levels in serum of children with AD, associated with rhinitis and/or asthma
AD: atopic dermatitis; UBD: ubiquitin D; IFN-g: interferon-g; CCL: chemokine ligand; NF-kB: nuclear factor kappa B
contrary, the expression of miR-125b was decreased gene expression regulators could potentially be used
significantly in both psoriasis and AD [26] . Another as personalized therapeutics in the near future.
interesting observation in that study was that miR-
203 was expressed more than 100-fold higher in skin DECLARATIONS
compared to other organs, including esophagus and
cervix that contain squamous epithelium. However, Authors’ contributions
mature forms of miR-146a, miR-21 and miR-125b were N. Bhardwaj contributed solely to the paper.
detectable in all studied organs. A synopsis of the
major miRNA players in atopic dermatitis is provided Financial support and sponsorship
in Table 1. None.
Since their discovery in mammalian cells approximately Conflicts of interest
10 years ago, the role of miRNAs in immune system There are no conflicts of interest.
has been extensively studied. MiRNAs can be
detected in different cell-free body fluids, such as Patient consent
serum, plasma, urine and saliva. This obviously raises Not applicable.
the question whether serum miRNAs can be used as
biomarkers of disease. Numerous studies have shown Ethics approval
that miRNAs can be used as diagnostic as well as Not applicable.
prognostic markers in various cancers, tissue injury
and inflammation. The connection between miRNAs
and allergic inflammatory conditions such as asthma, REFERENCES
allergic rhinitis and eosinophilic esophagitis is being
extensively investigated. Only a few studies have 1. Schmitt J, Langan S, Deckert S, Svensson A, von Kobyletzki L,
delved into the role of miRNAs in atopic dermatitis. Thomas K, Spuls P; Harmonising Outcome Measures for Atopic
Dermatitis (HOME) Initiative. Assessment of clinical signs of atopic
While we are learning about the expression profile dermatitis: a systematic review and recommendation. J Allergy Clin
of miRNAs in inflammatory skin conditions and their Immunol 2013;132:1337-47.
impact on inflammation, the question that needs to 2. Shaw TE, Currie GP, Koudelka CW, Simpson EL. Eczema prevalence
be answered is what drives this aberrant expression. in the United States: data from the 2003 National Survey of Children’s
Considering their role as master switches of complex Health. J Invest Dermatol 2011;131:67-73.
cellular processes, they could be potential therapeutic 3. Spergel JM. From atopic dermatitis to asthma: the atopic march. Ann
targets for inflammatory skin conditions including 4. Allergy Asthma Immunol 2010;105:99-106; quiz 107-9, 117.
Spergel JM, Paller AS. Atopic dermatitis and the atopic march. J
atopic dermatitis. A potential challenge with biological Allergy Clin Immunol 2003;112:S118-27.
treatments is the inbuilt redundancy in signaling 5. Leung DY, Guttman-Yassky E. Deciphering the complexities of atopic
pathways which allows natural compensation dermatitis: shifting paradigms in treatment approaches. J Allergy Clin
of effects of biologics targeting single genes or Immunol 2014;134:769-79.
proteins. MiRNAs, however, target multiple genes 6. Gittler JK, Shemer A, Suárez-Fariñas M, Fuentes-Duculan J, Gulewicz
simultaneously, hence, may offer an opportunity to KJ, Wang CQ, Mitsui H, Cardinale I, de Guzman Strong C, Krueger
modulate the functioning of whole pathways rather JG, Guttman-Yassky E. Progressive activation of T(H)2/T(H)22
cytokines and selective epidermal proteins characterizes acute and
than individual components. With accumulating chronic atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2012;130:1344-54.
knowledge about the role of miRNAs in inflammation, 7. Bieber T. Atopic dermatitis. N Engl J Med 2008;358:1483-94.
along with development of safe, effective and specific 8. Park H, Li Z, Yang XO, Chang SH, Nurieva R, Wang YH, Wang
methods of miRNA delivery systems, these novel Y, Hood L, Zhu Z, Tian Q, Dong C. A distinct lineage of CD4 T
20 Journal of Translational Genetics and Genomics ¦ Volume 1 ¦ November 17, 2017