Page 10 - Read Online
P. 10
Bhardwaj MicroRNAs in atopic dermatitis
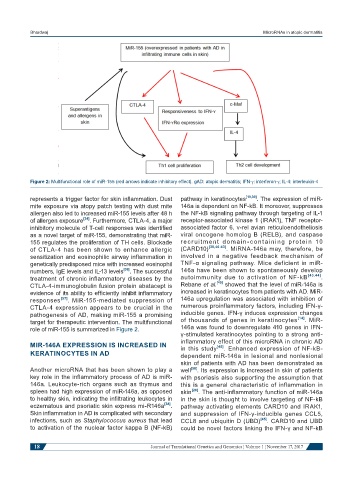
Figure 2: Multifunctional role of miR-155 (red arrows indicate inhibitory effect). gAD: atopic dermatitis; IFN-g: interferon-g; IL-4: interleukin-4
represents a trigger factor for skin inflammation. Dust pathway in keratinocytes [19,39] . The expression of miR-
mite exposure via atopy patch testing with dust mite 146a is dependent on NF-kB. It moreover, suppresses
allergen also led to increased miR-155 levels after 48 h the NF-kB signaling pathway through targeting of IL-1
of allergen exposure [34] . Furthermore, CTLA-4, a major receptor-associated kinase 1 (IRAK1), TNF receptor-
inhibitory molecule of T-cell responses was identified associated factor 6, v-rel avian reticuloendotheliosis
as a novel target of miR-155, demonstrating that miR- viral oncogene homolog B (RELB), and caspase
155 regulates the proliferation of TH cells. Blockade rec r uitment domain - c ont aining protein 10
of CTLA-4 has been shown to enhance allergic (CARD10) [38,40-43] . MiRNA-146a may, therefore, be
sensitization and eosinophilic airway inflammation in involved in a negative feedback mechanism of
genetically predisposed mice with increased eosinophil TNF-α signaling pathway. Mice deficient in miR-
numbers, IgE levels and IL-13 levels [36] . The successful 146a have been shown to spontaneously develop
treatment of chronic inflammatory diseases by the autoimmunity due to activation of NF-kB [43,44] .
CTLA-4-immunoglobulin fusion protein abatacept is Rebane et al. [45] showed that the level of miR-146a is
evidence of its ability to efficiently inhibit inflammatory increased in keratinocytes from patients with AD. MiR-
responses [37] . MiR-155-mediated suppression of 146a upregulation was associated with inhibition of
CTLA-4 expression appears to be crucial in the numerous proinflammatory factors, including IFN-γ-
pathogenesis of AD, making miR-155 a promising inducible genes. IFN-γ induces expression changes
[14]
target for therapeutic intervention. The multifunctional of thousands of genes in keratinocytes . MiR-
role of miR-155 is summarized in Figure 2. 146a was found to downregulate 410 genes in IFN-
γ-stimulated keratinocytes pointing to a strong anti-
MIR-146A EXPRESSION IS INCREASED IN inflammatory effect of this microRNA in chronic AD
[45]
in this study
. Enhanced expression of NF-kB-
KERATINOCYTES IN AD dependent miR-146a in lesional and nonlesional
skin of patients with AD has been demonstrated as
Another microRNA that has been shown to play a well [38] . Its expression is increased in skin of patients
key role in the inflammatory process of AD is miR- with psoriasis also supporting the assumption that
146a. Leukocyte-rich organs such as thymus and this is a general characteristic of inflammation in
spleen had high expression of miR-146a, as opposed skin [26] . The anti-inflammatory function of miR-146a
to healthy skin, indicating the infiltrating leukocytes in in the skin is thought to involve targeting of NF-kB
eczematous and psoriatic skin express mi-R146a [38] . pathway activating elements CARD10 and IRAK1,
Skin inflammation in AD is complicated with secondary and suppression of IFN-γ-inducible genes CCL5,
infections, such as Staphylococcus aureus that lead CCL8 and ubiquitin D (UBD) [45] . CARD10 and UBD
to activation of the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kB) could be novel factors linking the IFN-γ and NF-kB
18 Journal of Translational Genetics and Genomics ¦ Volume 1 ¦ November 17, 2017