Page 11 - Read Online
P. 11
Bhardwaj MicroRNAs in atopic dermatitis
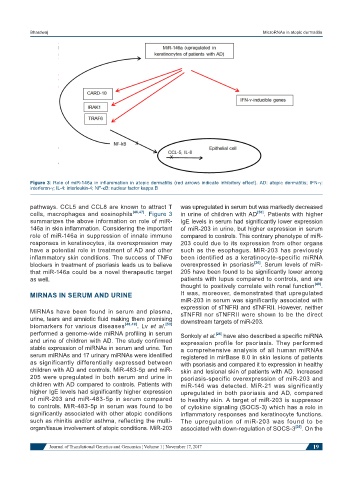
Figure 3: Role of miR-146a in inflammation in atopic dermatitis (red arrows indicate inhibitory effect). AD: atopic dermatitis; IFN-g:
interferon-g; IL-4: interleukin-4; NF-kB: nuclear factor kappa B
pathways. CCL5 and CCL8 are known to attract T was upregulated in serum but was markedly decreased
cells, macrophages and eosinophils [46,47] . Figure 3 in urine of children with AD [50] . Patients with higher
summarizes the above information on role of miR- IgE levels in serum had significantly lower expression
146a in skin inflammation. Considering the important of miR-203 in urine, but higher expression in serum
role of miR-146a in suppression of innate immune compared to controls. This contrary phenotype of miR-
responses in keratinocytes, its overexpression may 203 could due to its expression from other organs
have a potential role in treatment of AD and other such as the esophagus. MiR-203 has previously
inflammatory skin conditions. The success of TNFα been identified as a keratinocyte-specific miRNA
blockers in treatment of psoriasis leads us to believe overexpressed in psoriasis [26] . Serum levels of miR-
that miR-146a could be a novel therapeutic target 205 have been found to be significantly lower among
as well. patients with lupus compared to controls, and are
thought to positively correlate with renal function [49] .
MIRNAS IN SERUM AND URINE It was, moreover, demonstrated that upregulated
miR-203 in serum was significantly associated with
expression of sTNFRI and sTNFRII. However, neither
MiRNAs have been found in serum and plasma, sTNFRI nor sTNFRII were shown to be the direct
urine, tears and amniotic fluid making them promising downstream targets of miR-203.
biomarkers for various diseases [48,49] . Lv et al. [50]
performed a genome-wide miRNA profiling in serum Sonkoly et al. [26] have also described a specific miRNA
and urine of children with AD. The study confirmed expression profile for psoriasis. They performed
stable expression of miRNAs in serum and urine. Ten a comprehensive analysis of all human miRNAs
serum miRNAs and 17 urinary miRNAs were identified registered in mirBase 8.0 in skin lesions of patients
as significantly differentially expressed between with psoriasis and compared it to expression in healthy
children with AD and controls. MiR-483-5p and miR- skin and lesional skin of patients with AD. Increased
205 were upregulated in both serum and urine in psoriasis-specific overexpression of miR-203 and
children with AD compared to controls. Patients with miR-146 was detected. MiR-21 was significantly
higher IgE levels had significantly higher expression upregulated in both psoriasis and AD, compared
of miR-203 and miR-483-5p in serum compared to healthy skin. A target of miR-203 is suppressor
to controls. MiR-483-5p in serum was found to be of cytokine signaling (SOCS-3) which has a role in
significantly associated with other atopic conditions inflammatory responses and keratinocyte functions.
such as rhinitis and/or asthma, reflecting the multi- The upregulation of miR-203 was found to be
organ/tissue involvement of atopic conditions. MiR-203 associated with down-regulation of SOCS-3 [26] . On the
Journal of Translational Genetics and Genomics ¦ Volume 1 ¦ November 17, 2017 19