Page 9 - Read Online
P. 9
Bhardwaj MicroRNAs in atopic dermatitis
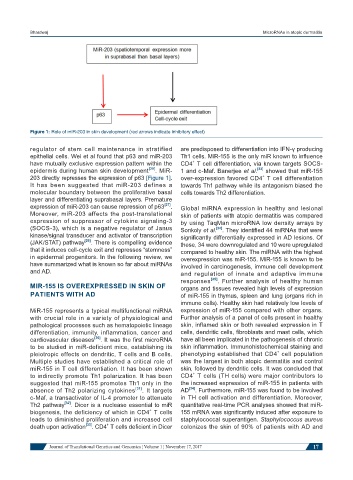
Figure 1: Role of miR-203 in skin development (red arrows indicate inhibitory effect)
regulator of stem cell maintenance in stratified are predisposed to differentiation into IFN-γ producing
epithelial cells. Wei et al found that p63 and miR-203 Th1 cells. MiR-155 is the only miR known to influence
+
have mutually exclusive expression pattern within the CD4 T cell differentiation, via known targets SOCS-
epidermis during human skin development [29] . MiR- 1 and c-Maf. Banerjee et al. [33] showed that miR-155
+
203 directly represses the expression of p63 [Figure 1]. over-expression favored CD4 T cell differentiation
It has been suggested that miR-203 defines a towards Th1 pathway while its antagonism biased the
molecular boundary between the proliferative basal cells towards Th2 differentiation.
layer and differentiating suprabasal layers. Premature
expression of miR-203 can cause repression of p63 [27] . Global miRNA expression in healthy and lesional
Moreover, miR-203 affects the post-translational skin of patients with atopic dermatitis was compared
expression of suppressor of cytokine signaling-3 by using TaqMan microRNA low density arrays by
(SOCS-3), which is a negative regulator of Janus Sonkoly et al. [34] . They identified 44 miRNAs that were
kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription significantly differentially expressed in AD lesions. Of
(JAK/STAT) pathway [26] . There is compelling evidence these, 34 were downregulated and 10 were upregulated
that it induces cell-cycle exit and represses “stemness” compared to healthy skin. The miRNA with the highest
in epidermal progenitors. In the following review, we overexpression was miR-155. MiR-155 is known to be
have summarized what is known so far about miRNAs involved in carcinogenesis, immune cell development
and AD. and regulation of innate and adaptive immune
responses [35] . Further analysis of healthy human
MIR-155 IS OVEREXPRESSED IN SKIN OF organs and tissues revealed high levels of expression
PATIENTS WITH AD of miR-155 in thymus, spleen and lung (organs rich in
immune cells). Healthy skin had relatively low levels of
MiR-155 represents a typical multifunctional miRNA expression of miR-155 compared with other organs.
with crucial role in a variety of physiological and Further analysis of a panel of cells present in healthy
pathological processes such as hematopoietic lineage skin, inflamed skin or both revealed expression in T
differentiation, immunity, inflammation, cancer and cells, dendritic cells, fibroblasts and mast cells, which
cardiovascular diseases [30] . It was the first microRNA have all been implicated in the pathogenesis of chronic
to be studied in miR-deficient mice, establishing its skin inflammation. Immunohistochemical staining and
+
pleiotropic effects on dendritic, T cells and B cells. phenotyping established that CD4 cell population
Multiple studies have established a critical role of was the largest in both atopic dermatitis and control
miR-155 in T cell differentiation. It has been shown skin, followed by dendritic cells. It was concluded that
+
to indirectly promote Th1 polarization. It has been CD4 T cells (TH cells) were major contributors to
suggested that miR-155 promotes Th1 only in the the increased expression of miR-155 in patients with
absence of Th2 polarizing cytokines [31] . It targets AD [34] . Furthermore, miR-155 was found to be involved
c-Maf, a transactivator of IL-4 promoter to attenuate in TH cell activation and differentiation. Moreover,
Th2 pathway [32] . Dicer is a nuclease essential to miR quantitative real-time PCR analyses showed that miR-
+
biogenesis, the deficiency of which in CD4 T cells 155 mRNA was significantly induced after exposure to
leads to diminished proliferation and increased cell staphylococcal superantigen. Staphylococcus aureus
death upon activation [33] . CD4 T cells deficient in Dicer colonizes the skin of 90% of patients with AD and
+
Journal of Translational Genetics and Genomics ¦ Volume 1 ¦ November 17, 2017 17