Page 182 - Read Online
P. 182
Liu et al. Th17 activation by H. pylori and triglyceride
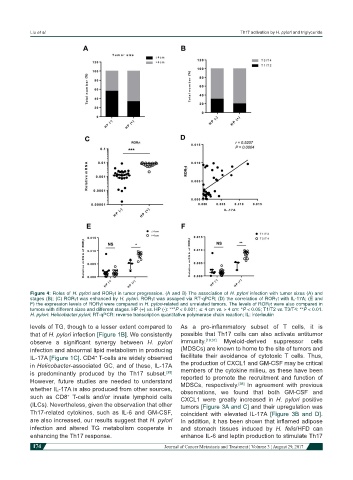
Figure 4: Roles of H. pylori and RORγt in tumor progression. (A and B) The association of H. pylori infection with tumor sizes (A) and
stages (B); (C) RORγt was enhanced by H. pylori. RORγt was assayed via RT-qPCR; (D) the correlation of RORγt with IL-17A; (E and
F) the expression levels of RORγt were compared in H. pylori-related and unrelated tumors. The levels of RORγt were also compared in
tumors with different sizes and different stages. HP (+) vs. HP (-): ***P < 0.001; ≤ 4 cm vs. > 4 cm: *P < 0.05; T1/T2 vs. T3/T4: **P < 0.01.
H. pylori: Helicobacter pylori; RT-qPCR: reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction; IL: interleukin
levels of TG, though to a lesser extent compared to As a pro-inflammatory subset of T cells, it is
that of H. pylori infection [Figure 1B]. We consistently possible that Th17 cells can also activate antitumor
observe a significant synergy between H. pylori immunity. [19,37] Myeloid-derived suppressor cells
infection and abnormal lipid metabolism in producing (MDSCs) are known to home to the site of tumors and
IL-17A [Figure 1C]. CD4 T-cells are widely observed facilitate their avoidance of cytotoxic T cells. Thus,
+
in Helicobacter-associated GC, and of these, IL-17A the production of CXCL1 and GM-CSF may be critical
is predominantly produced by the Th17 subset. [35] members of the cytokine milieu, as these have been
However, future studies are needed to understand reported to promote the recruitment and function of
MDSCs, respectively. In agreement with previous
[38]
whether IL-17A is also produced from other sources, observations, we found that both GM-CSF and
such as CD8 T-cells and/or innate lymphoid cells CXCL1 were greatly increased in H. pylori positive
+
(ILCs). Nevertheless, given the observation that other tumors [Figure 3A and C] and their upregulation was
Th17-related cytokines, such as IL-6 and GM-CSF, coincident with elevated IL-17A [Figure 3B and D].
are also increased, our results suggest that H. pylori In addition, it has been shown that inflamed adipose
infection and altered TG metabolism cooperate in and stomach tissues induced by H. felis/HFD can
enhancing the Th17 response. enhance IL-6 and leptin production to stimulate Th17
174 Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 3 ¦ August 29, 2017