Page 142 - Read Online
P. 142
Sorrentino et al. Role of A 2B receptor in cancer
immune suppression in the tumor environment. mediating the immunosuppressive effects of adenosine
Recent evidence indicate that A receptor stimulation in the tumor tissue and the high therapeutic potential of
2B
promotes the release of FGF-2 and C-X-C motif blocking adenosine generation and the A -mediated
2A
chemokine ligand 12 (CXCL12) from tumor-associated effects, by using anti-CD73 monoclonal antibodies and
fibroblasts, [125] that contribute to promote tumor growth A selective antagonists, respectively, it is becoming
2A
and angiogenesis. [126] These effects are associated clear that A receptor may significantly affect tumor
2B
with reduced expression of fibroblast activation progression and metastasis. Its contribute to tumor
protein (FAP), a common marker of tumor-activated development and growth is most likely dependent
fibroblasts termed cancer-associated fibroblasts on its high expression levels on tumor cells, and/or
(CAF), that promote tumor growth enhancing tumor endothelial cells and/or other tumor-infiltrating cells, in
immune evasion and tumor vascularization. [127] A a rich adenosine environment.
2B
receptor-induced CXCL12 by tumor-associated
fibroblasts contributes to the pro-angiogenic effects of CONCLUSION
A receptor via CXCR4, suggesting a link between
2B
tumor fibroblasts and endothelial cells. [127] Moreover, Adenosine plays a critical role in tumor immunity,
fibroblasts express CD73, which is up-regulated under angiogenesis and metastasis process. Strategies
hypoxic conditions. [127] Altogether, these evidence aimed to inhibit tumor adenosine production and
suggest that in the context of tumor A receptor functions, by using CD73 inhibitors and selective
2B
contributes to mediate multiple effects of adenosine on blockade of A adenosine receptor, are effective for
2A
different types of cells that populate the tumor niche. cancer treatments, especially in combination with
Furthermore, blockade of A receptor modulates the chemotherapeutic agents and immune-checkpoints
2B
intra-tumoral levels of paracrine factors, which are inhibitors.
critical in regulating intercellular crosstalk in the tumor
microenvironment. Nonetheless, compelling evidence support the
role of A receptor subtype in contributing to the
2B
Although the predominant role of A receptor in pro-tumor effects of adenosine within the tumor
2A
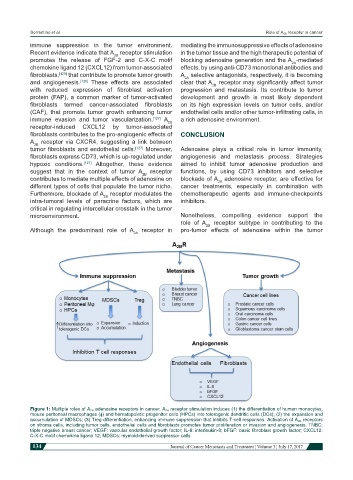
Figure 1: Multiple roles of A 2B adenosine receptors in cancer. A 2B receptor stimulation induces (1) the differentiation of human monocytes,
mouse peritoneal macrophages (φ) and hematopoietic progenitor cells (HPCs) into tolerogenic dendritic cells (DCs); (2) the expansion and
accumulation of MDSCs; (3) Treg differentiation, enhancing immune suppression that inhibits T-cell responses. Activation of A 2B receptors
on stroma cells, including tumor cells, endothelial cells and fibroblasts promotes tumor proliferation or invasion and angiogenesis. TNBC:
triple negative breast cancer; VEGF: vascular endothelial growth factor; IL-8: interleukin-8; bFGF: basic fibroblast growth factor; CXCL12:
C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 12; MDSCs: myeloid-derived suppressor cells
134 Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 3 ¦ July 17, 2017