Page 42 - Read Online
P. 42
Page 4 of 24 Saier et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2021;7:43 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2021.87
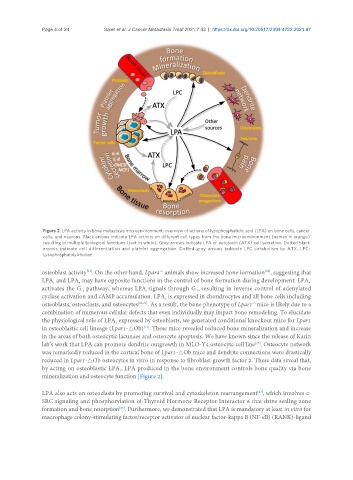
Figure 2. LPA activity in bone metastasis microenvironment: overview of actions of lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) on bone cells, cancer
cells, and neurons. Black arrows indicate LPA activity on different cell types from the bone microenvironment (names in orange)
resulting in multiple biological functions (text in white). Grey arrows indicate LPA or autotaxin (ATX) cell secretion. Dotted black
arrows indicate cell differentiation and platelet aggregation. Dotted grey arrows indicate LPC catabolism by ATX. LPC:
Lysophosphatidylcholine.
osteoblast activity . On the other hand, Lpar4 animals show increased bone formation , suggesting that
-/-
[22]
[21]
LPA and LPA may have opposite functions in the control of bone formation during development. LPA 4
4
1
activates the G pathway, whereas LPA signals through G , resulting in inverse control of adenylated
s
1
i
cyclase activation and cAMP accumulation. LPA is expressed in chondrocytes and all bone cells including
1
osteoblasts, osteoclasts, and osteocytes [21,23] . As a result, the bone phenotype of Lpar1 mice is likely due to a
-/-
combination of numerous cellular defects that even individually may impact bone remodeling. To elucidate
the physiological role of LPA expressed by osteoblasts, we generated conditional knockout mice for Lpar1
1
[17]
in osteoblastic cell lineage (Lpar1-△Ob) . These mice revealed reduced bone mineralization and increase
in the areas of both osteocytic lacunaes and osteocyte apoptosis. We have known since the release of Karin
[24]
lab’s work that LPA can promote dendrite outgrowth in MLO-Y4 osteocyte cell line . Osteocyte network
was remarkedly reduced in the cortical bone of Lpar1-△Ob mice and dendrite connections were drastically
reduced in Lpar1-△Ob osteocytes in vitro in response to fibroblast growth factor 2. These data reveal that,
by acting on osteoblastic LPA , LPA produced in the bone environment controls bone quality via bone
1
mineralization and osteocyte function [Figure 2].
[23]
LPA also acts on osteoclasts by promoting survival and cytoskeleton rearrangement , which involves c-
SRC signaling and phosphorylation of Thyroid Hormone Receptor Interactor 6 that drive sealing zone
formation and bone resorption . Furthermore, we demonstrated that LPA is mandatory at least in vitro for
[25]
macrophage colony-stimulating factor/receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) (RANK)-ligand