Page 51 - Read Online
P. 51
Page 8 of 13 Gambari et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2019;5:55 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2019.18
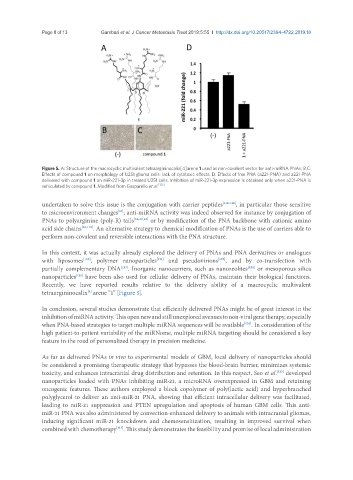
Figure 5. A: Structure of the macrocyclic multivalent tetraargininocalix[4]arene 1 used as non-covalent vector for anti-miRNA PNAs; B,C:
Effects of compound 1 on morphology of U251 glioma cells: lack of cytotoxic effects. D. Effects of free PNA (a221-PNA) and a221-PNA
delivered with compound 1 on miR-221-3p in treated U251 cells. Inhibition of miR-221-3p expression is obtained only when a221-PNA is
vehiculated by compound 1. Modified from Gasparello et al. [125]
undertaken to solve this issue is the conjugation with carrier peptides [116-118] , in particular those sensitive
to microenvironment changes ; anti-miRNA activity was indeed observed for instance by conjugation of
[11]
PNAs to polyarginine (poly-R) tails [58,59,62] or by modification of the PNA backbone with cationic amino
acid side chains [58,119] . An alternative strategy to chemical modification of PNAs is the use of carriers able to
perform non-covalent and reversible interactions with the PNA structure.
In this context, it was actually already explored the delivery of PNAs and PNA derivatives or analogues
with liposomes , polymer nanoparticles and pseudovirions , and by co-transfection with
[121]
[122]
[120]
partially complementary DNA . Inorganic nanocarriers, such as nanozeolites or mesoporous silica
[123]
[124]
nanoparticles have been also used for cellular delivery of PNAs, maintain their biological functions.
[111]
Recently, we have reported results relative to the delivery ability of a macrocyclic multivalent
tetraargininocalix arene “1” [Figure 5].
[4]
In conclusion, several studies demonstrate that efficiently delivered PNAs might be of great interest in the
inhibition of miRNA activity. This open new and still unexplored avenues to non-viral gene therapy, especially
when PNA-based strategies to target multiple miRNA sequences will be available . In consideration of the
[126]
high patient-to-patient variability of the miRNome, multiple miRNA targeting should be considered a key
feature in the road of personalized therapy in precision medicine.
As far as delivered PNAs in vivo to experimental models of GBM, local delivery of nanoparticles should
be considered a promising therapeutic strategy that bypasses the blood-brain barrier, minimizes systemic
toxicity, and enhances intracranial drug distribution and retention. In this respect, Seo et al. developed
[113]
nanoparticles loaded with PNAs inhibiting miR-21, a microRNA overexpressed in GBM and retaining
oncogenic features. These authors employed a block copolymer of poly(lactic acid) and hyperbranched
polyglycerol to deliver an anti-miR-21 PNA, showing that efficient intracellular delivery was facilitated,
leading to miR-21 suppression and PTEN upregulation and apoptosis of human GBM cells. This anti-
miR-21 PNA was also administered by convection-enhanced delivery to animals with intracranial gliomas,
inducing significant miR-21 knockdown and chemosensitization, resulting in improved survival when
combined with chemotherapy . This study demonstrates the feasibility and promise of local administration
[113]