Page 46 - Read Online
P. 46
Gambari et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2019;5:55 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2019.18 Page 3 of 13
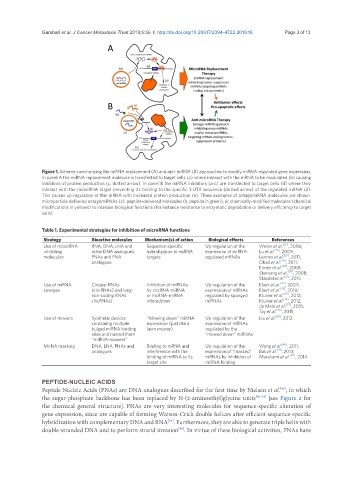
Figure 1. Scheme summarizing the miRNA replacement (A) and anti-miRNA (B) approaches to modify miRNA-regulated gene expression.
In panel A the miRNA replacement molecule is transfected to target cells (a) where interact with the mRNA to be modulated (b) causing
inhibition of protein production (c, dotted arrow). In panel B the miRNA inhibitors (a-c) are transfected to target cells (d) where they
interact with the microRNA target preventing its binding to the specific 3’UTR sequence (dotted arrow) of the regulated mRNA (d).
This causes up-regulation of this mRNA with increased protein production (e). Three examples of antagomiRNA molecules are shown:
microparticle delivered antagomiRNAs (a), peptide-delivered molecules (b, peptide in green), or chemically-modified molecules (chemical
modifications in yellows) to increase biological functions (for instance resistance to enzymatic degradation or delivery efficiency to target
cells)
Table 1. Experimental strategies for inhibition of microRNA functions
Strategy Bioactive molecules Mechanism(s) of action Biological effects References
Use of microRNA RNA, DNA, LNA and Sequence-specific Up-regulation of the Weiler et al. [25] , 2006;
inhibiting other DNA analogues, hybridization to miRNA expression of miRNA- Lu et al. [26] , 2009;
molecules PNAs and PNA targets regulated mRNAs Lennox et al. [27] , 2011;
analogues Obad et al. [28] , 2011;
Elmén et al. [29] , 2008;
Stenvang et al. [30] , 2008;
[31]
Staedel et al. , 2015
Use of miRNA Circular RNAs Inhibition of miRNAs Up-regulation of the Ebert et al. [32] , 2007;
sponges (circRNAs) and long- by circRNA-miRNA expression of mRNAs Ebert et al. [33] , 2010;
non-coding RNAs or lncRNA-miRNA regulated by sponged Kluiver et al. [34] , 2012;
(lncRNAs) interactions miRNAs Kluiver et al. [35] , 2012;
de Melo et al. [37] , 2015;
Tay et al. [38] , 2015
Use of mowers Synthetic devices ‘‘Mowing down’’ miRNA Up-regulation of the Liu et al. [39] , 2012
containing multiple expression (just like a expression of mRNAs
bulged miRNA binding lawn mower) regulated by the
sites and named them “mowed down” miRNAs
‘‘miRNA-mowers’’
MirNA masking DNA, LNA, PNAs and Binding to mRNA and Up-regulation of the Wang et al. [40] , 2011;
analogues interference with the expression of “masked” Bak et al. [41] , 2013;
binding of miRNA to its mRNAs by inhibition of Murakami et al. [42] , 2014
target site miRNA binding
PEPTIDE-NUCLEIC ACIDS
Peptide Nucleic Acids (PNAs) are DNA analogues described for the first time by Nielsen et al. , in which
[49]
the sugar-phosphate backbone has been replaced by N-(2-aminoethyl)glycine units [50-53] [see Figure 2 for
the chemical general structure]. PNAs are very interesting molecules for sequence-specific alteration of
gene expression, since are capable of forming Watson-Crick double helices after efficient sequence-specific
hybridization with complementary DNA and RNA . Furthermore, they are able to generate triple helix with
[54]
double-stranded DNA and to perform strand invasion . In virtue of these biological activities, PNAs have
[55]