Page 50 - Read Online
P. 50
Gambari et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2019;5:55 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2019.18 Page 7 of 13
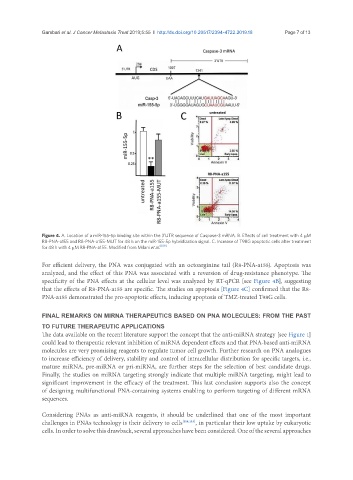
Figure 4. A. Location of a miR-155-5p binding site within the 3’UTR sequence of Caspase-3 mRNA. B. Effects of cell treatment with 4 µM
R8-PNA-a155 and R8-PNA-a155-MUT for 48 h on the miR-155-5p hybridization signal. C. Increase of T98G apoptotic cells after treatment
for 48 h with 4 µM R8-PNA-a155. Modified from Milani et al. [109]
For efficient delivery, the PNA was conjugated with an octoarginine tail (R8-PNA-a155). Apoptosis was
analyzed, and the effect of this PNA was associated with a reversion of drug-resistance phenotype. The
specificity of the PNA effects at the cellular level was analyzed by RT-qPCR [see Figure 4B], suggesting
that the effects of R8-PNA-a155 are specific. The studies on apoptosis [Figure 4C] confirmed that the R8-
PNA-a155 demonstrated the pro-apoptotic effects, inducing apoptosis of TMZ-treated T98G cells.
FINAL REMARKS ON MIRNA THERAPEUTICS BASED ON PNA MOLECULES: FROM THE PAST
TO FUTURE THERAPEUTIC APPLICATIONS
The data available on the recent literature support the concept that the anti-miRNA strategy [see Figure 1]
could lead to therapeutic relevant inhibition of miRNA dependent effects and that PNA-based anti-miRNA
molecules are very promising reagents to regulate tumor cell growth. Further research on PNA analogues
to increase efficiency of delivery, stability and control of intracellular distribution for specific targets, i.e.,
mature miRNA, pre-miRNA or pri-miRNA, are further steps for the selection of best candidate drugs.
Finally, the studies on miRNA targeting strongly indicate that multiple miRNA targeting, might lead to
significant improvement in the efficacy of the treatment. This last conclusion supports also the concept
of designing multifunctional PNA-containing systems enabling to perform targeting of different mRNA
sequences.
Considering PNAs as anti-miRNA reagents, it should be underlined that one of the most important
challenges in PNAs technology is their delivery to cells [114,115] , in particular their low uptake by eukaryotic
cells. In order to solve this drawback, several approaches have been considered. One of the several approaches