Page 380 - Read Online
P. 380
Verkoeijen et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2019;5:51 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2019.06 Page 9 of 16
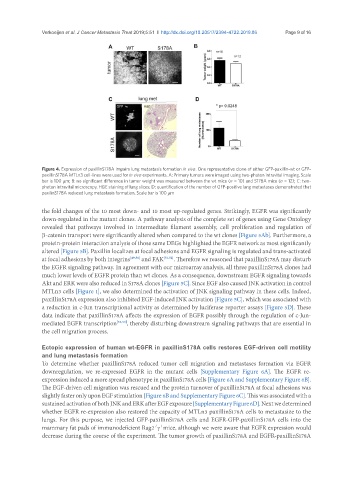
Figure 4. Expression of paxillinS178A impairs lung metastasis formation in vivo. One representative clone of either GFP-paxillin-wt or GFP-
paxillinS178A MTLn3 cell-lines were used for in vivo experiments. A: Primary tumors were imaged using two-photon intravital imaging. Scale
bar is 100 mm; B: no significant difference in tumor weight was measured between the wt mice (n = 10) and S178A mice (n = 12); C: two-
photon intravital microscopy, H&E staining of lung slices; D: quantification of the number of GFP-positive lung metastases demonstrated that
paxilinS178A reduced lung metastasis formation. Scale bar is 100 mm
the fold changes of the 10 most down- and 10 most up-regulated genes. Strikingly, EGFR was significantly
down-regulated in the mutant clones. A pathway analysis of the complete set of genes using Gene Ontology
revealed that pathways involved in intermediate filament assembly, cell proliferation and regulation of
β-catenin transport were significantly altered when compared to the wt clones [Figure 5Ab]. Furthermore, a
protein-protein interaction analysis of those same DEGs highlighted the EGFR network as most significantly
altered [Figure 5B]. Paxillin localizes at focal adhesions and EGFR signaling is regulated and trans-activated
at focal adhesions by both integrins [49,50] and FAK [51,52] . Therefore we reasoned that paxillinS178A may disturb
the EGFR signaling pathway. In agreement with our microarray analysis, all three paxillinS178A clones had
much lower levels of EGFR protein than wt clones. As a consequence, downstream EGFR signaling towards
Akt and ERK were also reduced in S178A clones [Figure 5C]. Since EGF also caused JNK activation in control
MTLn3 cells [Figure 1], we also determined the activation of JNK signaling pathway in these cells. Indeed,
paxillinS178A expression also inhibited EGF-induced JNK activation [Figure 5C], which was associated with
a reduction in c-Jun transcriptional activity as determined by luciferase reporter assays [Figure 5D]. These
data indicate that paxillinS178A affects the expression of EGFR possibly through the regulation of c-Jun-
mediated EGFR transcription [53,54] , thereby disturbing downstream signaling pathways that are essential in
the cell migration process.
Ectopic expression of human wt-EGFR in paxillinS178A cells restores EGF-driven cell motility
and lung metastasis formation
To determine whether paxillinS178A reduced tumor cell migration and metastases formation via EGFR
downregulation, we re-expressed EGFR in the mutant cells [Supplementary Figure 6A]. The EGFR re-
expression induced a more spread phenotype in paxillinS178A cells [Figure 6A and Supplementary Figure 6B].
The EGF-driven cell migration was rescued and the protein turnover of paxillinS178A at focal adhesions was
slightly faster only upon EGF stimulation [Figure 6B and Supplementary Figure 6C]. This was associated with a
sustained activation of both JNK and ERK after EGF exposure [Supplementary Figure 6D]. Next we determined
whether EGFR re-expression also restored the capacity of MTLn3 paxillinS178A cells to metastasize to the
lungs. For this purpose, we injected GFP-paxillinS178A cells and EGFR-GFP-paxillinS178A cells into the
mammary fat pads of immunodeficient Rag2 g mice, although we were aware that EGFR expression would
-/- -/-
decrease during the course of the experiment. The tumor growth of paxillinS178A and EGFR-paxillinS178A