Page 378 - Read Online
P. 378
Verkoeijen et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2019;5:51 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2019.06 Page 7 of 16
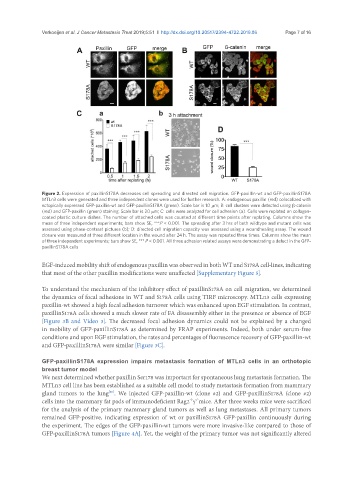
Figure 2. Expression of paxillinS178A decreases cell spreading and directed cell migration. GFP-paxillin-wt and GFP-paxillinS178A
MTLn3 cells were generated and three independent clones were used for further research. A: endogenous paxillin (red) colocalized with
ectopically expressed GFP-paxillin-wt and GFP-paxillinS178A (green). Scale bar is 10 mm; B: cell clusters were detected using β-catenin
(red) and GFP-paxillin (green) staining. Scale bar is 20 mm; C: cells were analyzed for cell adhesion (a). Cells were replated on collagen-
coated plastic culture dishes. The number of attached cells was counted at different time points after replating. Columns show the
mean of three independent experiments; bars show SE, ***P < 0.001. The spreading after 3 hrs of both wildtype and mutant cells was
assessed using phase-contrast pictures (b); D: directed cell migration capacity was assessed using a woundhealing assay. The wound
closure was measured at three different location in the wound after 24 h. The assay was repeated three times. Columns show the mean
of three independent experiments; bars show SE, *** P < 0.001. All three adhesion related assays were demonstrating a defect in the GFP-
paxillinS178A cells
EGF-induced mobility shift of endogenous paxillin was observed in both WT and S178A cell-lines, indicating
that most of the other paxillin modifications were unaffected [Supplementary Figure 5].
To understand the mechanism of the inhibitory effect of paxillinS178A on cell migration, we determined
the dynamics of focal adhesions in WT and S178A cells using TIRF microscopy. MTLn3 cells expressing
paxillin-wt showed a high focal adhesion turnover which was enhanced upon EGF stimulation. In contrast,
paxillinS178A cells showed a much slower rate of FA disassembly either in the presence or absence of EGF
[Figure 3B and Video 3]. The decreased focal adhesion dynamics could not be explained by a changed
in mobility of GFP-paxillinS178A as determined by FRAP experiments. Indeed, both under serum-free
conditions and upon EGF stimulation, the rates and percentages of fluorescence recovery of GFP-paxillin-wt
and GFP-paxillinS178A were similar [Figure 3C].
GFP-paxillinS178A expression impairs metastasis formation of MTLn3 cells in an orthotopic
breast tumor model
We next determined whether paxillin Ser178 was important for spontaneous lung metastasis formation. The
MTLn3 cell line has been established as a suitable cell model to study metastasis formation from mammary
gland tumors to the lung . We injected GFP-paxillin-wt (clone #2) and GFP-paxillinS178A (clone #2)
[10]
-/- -/-
cells into the mammary fat pads of immunodeficient Rag2 g mice. After three weeks mice were sacrificed
for the analysis of the primary mammary gland tumors as well as lung metastases. All primary tumors
remained GFP-positive, indicating expression of wt or paxillinS178A GFP-paxillin continuously during
the experiment. The edges of the GFP-paxillin-wt tumors were more invasive-like compared to those of
GFP-paxillinS178A tumors [Figure 4A]. Yet, the weight of the primary tumor was not significantly altered