Page 384 - Read Online
P. 384
Verkoeijen et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2019;5:51 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2019.06 Page 13 of 16
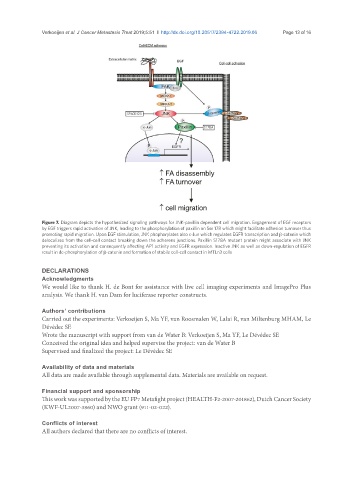
Figure 7. Diagram depicts the hypothesized signaling pathways for JNK-paxillin dependent cell migration. Engagement of EGF receptors
by EGF triggers rapid activation of JNK, leading to the phosphorylation of paxillin on Ser 178 which might facilitate adhesion turnover thus
promoting rapid migration. Upon EGF stimulation, JNK phophorylates also c-Jun which regulates EGFR transcription and β-catenin which
delocalizes from the cell-cell contact breaking down the adherens junctions. Paxillin S178A mutant protein might associate with JNK
preventing its activation and consequently affecting AP1 activity and EGFR expression. Inactive JNK as well as down-regulation of EGFR
result in de-phosphorylation of β-catenin and formation of stabile cell-cell contact in MTLn3 cells
DECLARATIONS
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank H. de Bont for assistance with live cell imaging experiments and ImagePro Plus
analysis. We thank H. van Dam for luciferase reporter constructs.
Authors’ contributions
Carried out the experiments: Verkoeijen S, Ma YF, van Roosmalen W, Lalai R, van Miltenburg MHAM, Le
Dévédec SE
Wrote the manuscript with support from van de Water B: Verkoeijen S, Ma YF, Le Dévédec SE
Conceived the original idea and helped supervise the project: van de Water B
Supervised and finalized the project: Le Dévédec SE
Availability of data and materials
All data are made available through supplemental data. Materials are available on request.
Financial support and sponsorship
This work was supported by the EU FP7 Metafight project (HEALTH-F2-2007-201862), Dutch Cancer Society
(KWF-UL2007-3860) and NWO grant (911-02-022).
Conflicts of interest
All authors declared that there are no conflicts of interest.