Page 78 - Read Online
P. 78
Pippione et al. Steroidogenic enzymes in prostate cancer
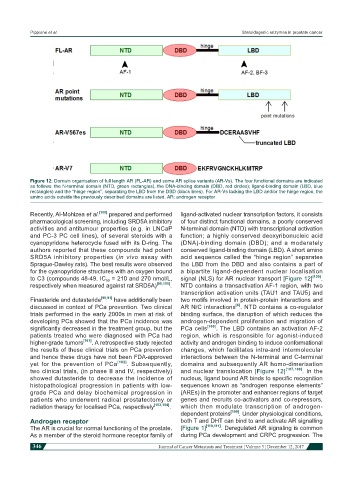
Figure 12: Domain organisation of full length AR (FL-AR) and some AR splice variants (AR-Vs). The four functional domains are indicated
as follows: the N-terminal domain (NTD, green rectangles), the DNA-binding domain (DBD, red circles); ligand-binding domain (LBD, blue
rectangles) and the “hinge region”, separating the LBD from the DBD (black lines). For AR-Vs lacking the LBD and/or the hinge region, the
amino acids outside the previously described domains are listed. AR: androgen receptor
Recently, Al-Mohizea et al. [100] prepared and performed ligand-activated nuclear transcription factors, it consists
pharmacological screening, including SRD5A inhibitory of four distinct functional domains, a poorly conserved
activities and antitumour properties (e.g. in LNCaP N-terminal domain (NTD) with transcriptional activation
and PC-3 PC cell lines), of several steroids with a function; a highly conserved deoxyribonucleic acid
cyanopyridone heterocycle fused with its D-ring. The (DNA)-binding domain (DBD); and a moderately
authors reported that these compounds had potent conserved ligand-binding domain (LBD). A short amino
SRD5A inhibitory properties (in vivo assay with acid sequence called the “hinge region” separates
Sprague-Dawley rats). The best results were observed the LBD from the DBD and also contains a part of
for the cyanopyridone structures with an oxygen bound a bipartite ligand-dependent nuclear localisation
to C3 (compounds 48-49, IC 50 = 210 and 270 nmol/L, signal (NLS) for AR nuclear transport [Figure 12] [105] .
respectively when measured against rat SRD5A) [95,100] . NTD contains a transactivation AF-1 region, with two
transcription activation units (TAU1 and TAU5) and
Finasteride and dutasteride [90,91] have additionally been two motifs involved in protein-protein interactions and
[6]
discussed in context of PCa prevention. Two clinical AR N/C interactions . NTD contains a co-regulator
trials performed in the early 2000s in men at risk of binding surface, the disruption of which reduces the
developing PCa showed that the PCa incidence was androgen-dependent proliferation and migration of
significantly decreased in the treatment group, but the PCa cells [106] . The LBD contains an activation AF-2
patients treated who were diagnosed with PCa had region, which is responsible for agonist-induced
higher-grade tumors [101] . A retrospective study rejected activity and androgen binding to induce conformational
the results of these clinical trials on PCa prevention changes, which facilitates intra-and intermolecular
and hence these drugs have not been FDA-approved interactions between the N-terminal and C-terminal
yet for the prevention of PCa [102] . Subsequently, domains and subsequently AR homo-dimerisation
two clinical trials, (in phase II and IV, respectively) and nuclear translocation [Figure 12] [107,108] . In the
showed dutasteride to decrease the incidence of nucleus, ligand bound AR binds to specific recognition
histopathological progression in patients with low- sequences known as “androgen response elements”
grade PCa and delay biochemical progression in (AREs) in the promoter and enhancer regions of target
patients who underwent radical prostatectomy or genes and recruits co-activators and co-repressors,
radiation therapy for localised PCa, respectively [103,104] . which then modulate transcription of androgen-
dependent proteins [109] . Under physiological conditions,
Androgen receptor both T and DHT can bind to and activate AR signalling
The AR is crucial for normal functioning of the prostate. [Figure 1] [110,111] . Deregulated AR signaling is common
As a member of the steroid hormone receptor family of during PCa development and CRPC progression. The
346 Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 3 ¦ December 12, 2017