Page 81 - Read Online
P. 81
Pippione et al. Steroidogenic enzymes in prostate cancer
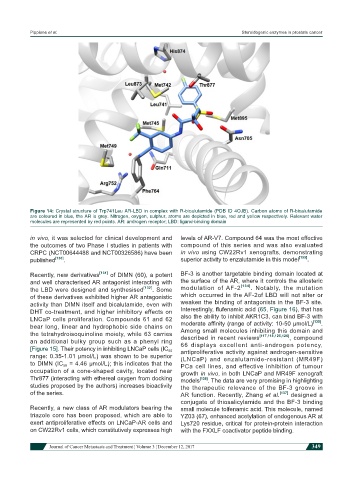
Figure 14: Crystal structure of Trp741Leu AR-LBD in complex with R-bicalutamide (PDB ID 4OJB). Carbon atoms of R-bicalutamide
are coloured in blue, the AR is grey. Nitrogen, oxygen, sulphur, atoms are depicted in blue, red and yellow respectively. Relevant water
molecules are represented by red points. AR: androgen receptor; LBD: ligand-binding domain
in vivo, it was selected for clinical development and levels of AR-V7. Compound 64 was the most effective
the outcomes of two Phase I studies in patients with compound of this series and was also evaluated
CRPC (NCT00644488 and NCT00326586) have been in vivo using CW22Rv1 xenografts, demonstrating
published [130] . superior activity to enzalutamide in this model [133] .
Recently, new derivatives [131] of DIMN (60), a potent BF-3 is another targetable binding domain located at
and well characterised AR antagonist interacting with the surface of the AR, where it controls the allosteric
[134]
the LBD were designed and synthesised [132] . Some modulation of AF-2 . Notably, the mutation
of these derivatives exhibited higher AR antagonistic which occurred in the AF-2of LBD will not alter or
activity than DIMN itself and bicalutamide, even with weaken the binding of antagonists in the BF-3 site.
DHT co-treatment, and higher inhibitory effects on Interestingly, flufenamic acid (65, Figure 16), that has
LNCaP cells proliferation. Compounds 61 and 62 also the ability to inhibit AKR1C3, can bind BF-3 with
[135]
bear long, linear and hydrophobic side chains on moderate affinity (range of activity: 10-50 µmol/L) .
the tetrahydroisoquinoline moiety, while 63 carries Among small molecules inhibiting this domain and
[117,118,125,126]
described in recent reviews
, compound
an additional bulky group such as a phenyl ring 66 displays excellent anti-androgen potency,
[Figure 15]. Their potency in inhibiting LNCaP cells (IC 50 antiproliferative activity against androgen-sensitive
range: 0.35-1.01 µmol/L) was shown to be superior (LNCaP) and enzalutamide-resistant (MR49F)
to DIMN (IC 50 = 4.46 µmol/L); this indicates that the PCa cell lines, and effective inhibition of tumour
occupation of a cone-shaped cavity, located near growth in vivo, in both LNCaP and MR49F xenograft
Thr877 (interacting with ethereal oxygen from docking models [136] . The data are very promising in highlighting
studies proposed by the authors) increases bioactivity the therapeutic relevance of the BF-3 groove in
of the series. AR function. Recently, Zhang et al. [137] designed a
conjugate of thiosalicylamide and the BF-3 binding
Recently, a new class of AR modulators bearing the small molecule tolfenamic acid. This molecule, named
triazole core has been proposed, which are able to YZ03 (67), enhanced acetylation of endogenous AR at
exert antiproliferative effects on LNCaP-AR cells and Lys720 residue, critical for protein-protein interaction
on CW22Rv1 cells, which constitutively expresses high with the FXXLF coactivator peptide binding.
Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 3 ¦ December 12, 2017 349