Page 258 - Read Online
P. 258
Cao Cancer Evo-Dev
A
Immune pressure in microenvironment
HBV genotype
HBV
mutations
HBV Balance of Activation of
integration oncogenic EMT HCC
Chronic inflammation AID/APOBECs signaling occurrence
inflammatory and UNGs
molecules De-differentiation
Somatic mutations
Genetic
predisposition
of key immune Epigenetic alterations
or inflammatory
molecules
B De-methylate the transcriptional factors for EMT
mtDNA Warburg
mutations effect
HBV genotype
HBV
mutations
HBV
integration Balance of Activation of HCC
Chronic inflammation AID/APOBECs oncogenic EMT occurrence
inflammatory and UNGs signaling
molecules De-differentiation
Somatic mutations
Genetic
predisposition
of key immune
or inflammatory Epigenetic alterations
molecules
Mt-ROS Mutation-selection-adaptation
C Androgen
AR
Inflammatory Somatic mutation Male
mediators
STAT3, etc. Balance of
Chronic inflammation AID/APOBECs Selection AR/FOXA Male
With DNA De-differentiation signalling cancer
repair
Cancers
Viral mutation
Interactions
of genetic
predisposition Estrogen
pro-inflammatory
molecules and
environmental
insults
Mutation--selection--adaptation
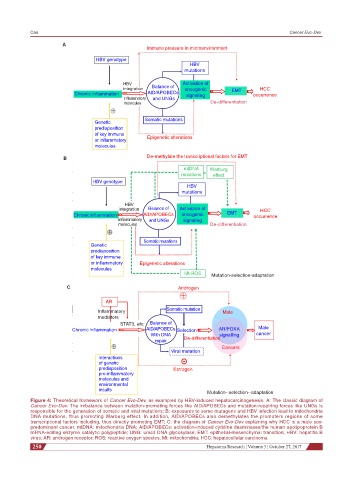
Figure 4: Theoretical framework of Cancer Evo-Dev, as exampled by HBV-induced hepatocarcinogenesis. A: The classic diagram of
Cancer Evo-Dev. The imbalance between mutation-promoting forces like AID/APOBECs and mutation-repairing forces like UNGs is
responsible for the generation of somatic and viral mutations; B: exposures to some mutagens and HBV infection lead to mitochondria
DNA mutations, thus promoting Warburg effect. In addition, AID/APOBECs also demethylates the promoters regions of some
transcriptional factors including, thus directly promoting EMT; C: the diagram of Cancer Evo-Dev explaining why HCC is a male sex-
predominant cancer. mtDNA: mitochondria DNA; AID/APOBECs: activation-induced cytidine deaminases/the human apolipoprotein B
mRNA-editing enzyme catalytic polypeptide; UNG: uracil DNA glycosylase; EMT: epithelial-mesenchymal transition; HBV: hepatitis B
virus; AR: androgen receptor; ROS: reactive oxygen species; Mt: mitochondria; HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma
250 Hepatoma Research ¦ Volume 3 ¦ October 27, 2017