Page 11 - Read Online
P. 11
Castán et al. Radiology of hepatocarcinoma in non-cirrhotic patients
Table 1: Magnetic resonance for the study of HCC appear with reduced signal with respect to the
Studies surrounding liver, because these tumors do not
FSPGR on phase and opposite phase enhanced on T1 express the hepatocyte sinusoidal transporter required
FRFSE enhanced on T2 fat-suppressed for uptake. [9]
LAVA or dynamic 3D SPGRE
Pre-contrast phase Ultrasonography
Post-contrast phase
Arterial phase: 16 s US is a non-invasive test and more accessible. It is
Portal phase: 60 s possible to determine the size and morphology of the
Late portal phase: 180 s lesion, its location, and possible vascular involvement.
Complementary phases: intermediate or later It also provides guidance for percutaneous biopsy.
Diffusion Its echogenicity is variable and non-specific and may
B Factor 0 and 600 seg/mm²
LAVA: liver acquisition with volume acceleration; HCC: be hypo- or hyperechoic. The largest lesions are more
hepatocellular carcinoma heterogeneous and often have hypo- or anechoic
necrotic areas. With Doppler color, central or peritumoral
differentiated and poorly differentiated tumors. It has
also been shown that atypical enhancement and A
clearing may even be seen in small HCC (< 2 cm). [6]
Magnetic resonance imaging
MRI is superior to CT in the diagnosis of HCC. The
study includes T2 sequences, dual phase-out of
phase, dynamic study and diffusion T1 sequences
[Table 1].
HCC presents variable signal intensity depending
on the degree of fibrosis, necrosis, and fat. It may
be hypo, iso, or hyperintense on T1 sequences. On
T2 it is generally hyperintense, especially with fat B
suppression sequences. Gadolinium enhancement
shows typical washing as described in CT:
enhancement in the arterial phase and typical clearing
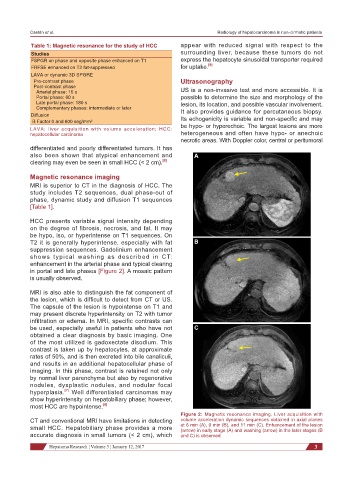
in portal and late phases [Figure 2]. A mosaic pattern
is usually observed.
MRI is also able to distinguish the fat component of
the lesion, which is difficult to detect from CT or US.
The capsule of the lesion is hypointense on T1 and
may present discrete hyperintensity on T2 with tumor
infiltration or edema. In MRI, specific contrasts can
be used, especially useful in patients who have not C
obtained a clear diagnosis by basic imaging. One
of the most utilized is gadoxectate disodium. This
contrast is taken up by hepatocytes, at approximate
rates of 50%, and is then excreted into bile canaliculi,
and results in an additional hepatocellular phase of
imaging. In this phase, contrast is retained not only
by normal liver parenchyma but also by regenerative
nodules, dysplastic nodules, and nodular focal
[7]
hyperplasia. Well differentiated carcinomas may
show hyperintensity on hepatobiliary phase; however,
most HCC are hypointense. [8]
Figure 2: Magnetic resonance imaging. Liver acquisition with
CT and conventional MRI have limitations in detecting volume acceleration dynamic sequences obtained in axial planes
small HCC. Hepatobiliary phase provides a more at 6 min (A), 9 min (B), and 11 min (C). Enhancement of the lesion
(arrow) in early stage (A) and washing (arrow) in the later stages (B
accurate diagnosis in small tumors (< 2 cm), which and C) is observed
Hepatoma Research ¦ Volume 3 ¦ January 12, 2017 3