Page 304 - Read Online
P. 304
Alves et al. Hepatocarcinoma with mediastinal metastasis
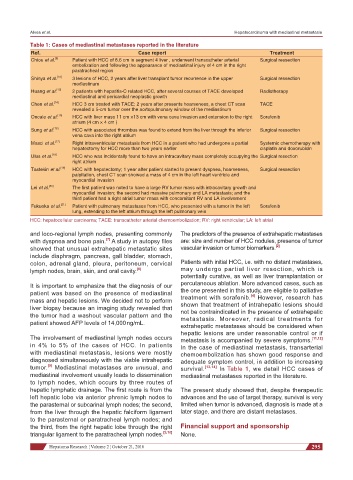
Table 1: Cases of mediastinal metastases reported in the literature
Ref. Case report Treatment
Chiou et al. [9] Patient with HCC of 8.6 cm in segment 4 liver , underwent transcatheter arterial Surgical ressection
embolization and following the appearance of mediastinal injury of 4 cm in the right
paratracheal region
Shinya et al. [10] 3 lesions of HCC, 2 years after liver transplant tumor recurrence in the upper Surgical ressection
mediastinum
Huang et al. [13] 2 patients with hepatitis-C related HCC, after several courses of TACE developed Radiotherapy
mediastinal and pericardial neoplastic growth
Chen et al. [14] HCC 3 cm treated with TACE; 2 years after presents hoarseness, a chest CT scan TACE
revealed a 5-cm tumor over the aortopulmonary window of the mediastinum
Oncale et al. [15] HCC with liver mass 11 cm ×13 cm with vena cava invasion and extension to the right Sorafenib
atrium (4 cm × 4 cm )
Sung et al. [16] HCC with associated thrombus was found to extend from the liver through the inferior Surgical ressection
vena cava into the right atrium
Masci et al. [17] Right intraventricular metastasis from HCC in a patient who had undergone a partial Systemic chemotherapy with
hepatectomy for HCC more than two years earlier cisplatin and doxorubicin
Ulus et al. [18] HCC who was incidentally found to have an intracavitary mass completely occupying the Surgical resection
right atrium
Tastekin et al. [19] HCC with hepatectomy; 1 year after patient started to present dyspnea, hoarseness, Surgical ressection
palpitation, chest CT scan showed a mass of 4 cm in the left heart ventricle and
myocardial invasion
Lei et al. [20] The first patient was noted to have a large RV tumor mass with intracavitary growth and
myocardial invasion; the second had massive pulmonary and LA metastasis; and the
third patient had a right atrial tumor mass with concomitant RV and LA involvement
Fukuoka et al. [21] Patient with pulmonary metastases from HCC, who presented with a tumor in the left Sorafenib
lung, extending to the left atrium through the left pulmonary vein
HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma; TACE: transcatheter arterial chemoembolization; RV: right ventricular; LA: left atrial
and loco-regional lymph nodes, presenting commonly The predictors of the presence of extrahepatic metastases
[7]
with dyspnea and bone pain. A study in autopsy files are: size and number of HCC nodules, presence of tumor
showed that unusual extrahepatic metastatic sites vascular invasion or tumor biomarkers. [2]
include diaphragm, pancreas, gall bladder, stomach,
colon, adrenal gland, pleura, peritoneum, cervical Patients with initial HCC, i.e. with no distant metastases,
lymph nodes, brain, skin, and oral cavity. [8] may undergo partial liver resection, which is
potentially curative, as well as liver transplantation or
It is important to emphasize that the diagnosis of our percutaneous ablation. More advanced cases, such as
patient was based on the presence of mediastinal the one presented in this study, are eligible to palliative
[4]
mass and hepatic lesions. We decided not to perform treatment with sorafenib. However, research has
liver biopsy because an imaging study revealed that shown that treatment of intrahepatic lesions should
not be contraindicated in the presence of extrahepatic
the tumor had a washout vascular pattern and the metastasis. Moreover, radical treatments for
patient showed AFP levels of 14,000 ng/mL. extrahepatic metastases should be considered when
hepatic lesions are under reasonable control or if
The involvement of mediastinal lymph nodes occurs metastasis is accompanied by severe symptoms. [11,12]
in 4% to 5% of the cases of HCC. In patients In the case of mediastinal metastasis, transarterial
with mediastinal metastasis, lesions were mostly chemoembolization has shown good response and
diagnosed simultaneously with the viable intrahepatic adequate symptom control, in addition to increasing
[9]
tumor. Mediastinal metastases are unusual, and survival. [13,14] In Table 1, we detail HCC cases of
mediastinal involvement usually leads to dissemination mediastinal metastases reported in the literature.
to lymph nodes, which occurs by three routes of
hepatic lymphatic drainage. The first route is from the The present study showed that, despite therapeutic
left hepatic lobe via anterior phrenic lymph nodes to advances and the use of target therapy, survival is very
the parasternal or subcarinal lymph nodes; the second, limited when tumor is advanced, diagnosis is made at a
from the liver through the hepatic falciform ligament later stage, and there are distant metastases.
to the parasternal or paratracheal lymph nodes; and
the third, from the right hepatic lobe through the right Financial support and sponsorship
triangular ligament to the paratracheal lymph nodes. [9,10] None.
Hepatoma Research ¦ Volume 2 ¦ October 21, 2016 295