Page 167 - Read Online
P. 167
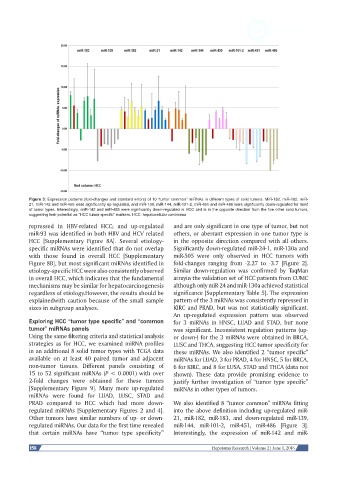
Figure 3: Expression patterns (fold-changes and standard errors) of 10 “tumor common” miRNAs in different types of solid tumors. MiR-182, miR-182, miR-
21, miR-142 and miR-455 were significantly up-regulated, and miR-139, miR-144, miR-101-2, miR-451 and miR-486 were significantly down-regulated for most
of tumor types. Interestingly, miR-142 and miR-455 were significantly down-regulated in HCC and is in the opposite direction from the five other solid tumors,
suggesting their potential as “HCC tumor specific” markers. HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma
repressed in HBV-related HCC; and up-regulated and are only significant in one type of tumor, but not
miR-93 was identified in both HBV and HCV related others, or aberrant expression in one tumor type is
HCC [Supplementary Figure 8A]. Several etiology- in the opposite direction compared with all others.
specific miRNAs were identified that do not overlap Significantly down-regulated miR-24-1, miR-130a and
with those found in overall HCC [Supplementary miR-505 were only observed in HCC tumors with
Figure 8B], but most significant miRNAs identified in fold-changes ranging from -2.27 to -3.7 [Figure 2].
etiology-specific HCC were also consistently observed Similar down-regulation was confirmed by TaqMan
in overall HCC, which indicates that the fundamental arrayin the validation set of HCC patients from CUMC
mechanisms may be similar for hepatocarcinogenesis although only miR-24 and miR-130a achieved statistical
regardless of etiology.However, the results should be significance [Supplementary Table 5]. The expression
explainedwith caution because of the small sample pattern of the 3 miRNAs was consistently repressed in
sizes in subgroup analyses. KIRC and PRAD, but was not statistically significant.
An up-regulated expression pattern was observed
Exploring HCC “tumor type specific” and “common for 3 miRNAs in HNSC, LUAD and STAD, but none
tumor” miRNAs panels was significant. Inconsistent regulation patterns (up-
Using the same filtering criteria and statistical analysis or down-) for the 3 miRNAs were obtained in BRCA,
strategies as for HCC, we examined miRNA profiles LUSC and THCA, suggesting HCC tumor specificity for
in an additional 8 solid tumor types with TCGA data these miRNAs. We also identified 2 “tumor specific”
available on at least 40 paired tumor and adjacent miRNAs for LUAD, 3 for PRAD, 4 for HNSC, 5 for BRCA,
non-tumor tissues. Different panels consisting of 6 for KIRC, and 8 for LUSA, STAD and THCA (data not
15 to 52 significant miRNAs (P < 0.0001) with over shown). These data provide promising evidence to
2-fold changes were obtained for these tumors justify further investigation of “tumor type specific”
[Supplementary Figure 9]. Many more up-regulated miRNAs in other types of tumors.
miRNAs were found for LUAD, LUSC, STAD and
PRAD compared to HCC which had more down- We also identified 8 “tumor common” miRNAs fitting
regulated miRNAs [Supplementary Figures 2 and 4]. into the above definition including up-regulated miR-
Other tumors have similar numbers of up- or down- 21, miR-182, miR-183, and down-regulated miR-139,
regulated miRNAs. Our data for the first time revealed miR-144, miR-101-2, miR-451, miR-486 [Figure 3].
that certain miRNAs have “tumor type specificity” Interestingly, the expression of miR-142 and miR-
158 Hepatoma Research | Volume 2 | June 1, 2016