Page 157 - Read Online
P. 157
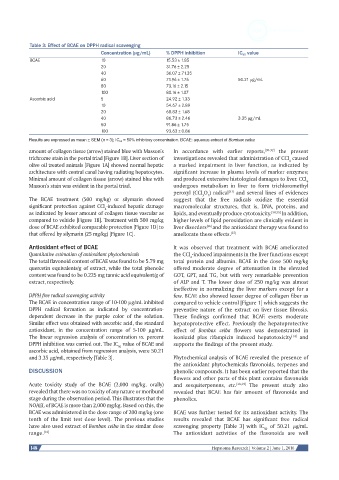
Table 3: Effect of BCAE on DPPH radical scavenging
Concentration (µg/mL) % DPPH inhibition IC 50 value
BCAE 10 15.53 ± 1.85
20 31.76 ± 2.25
40 36.07 ± 71.35
60 71.96 ± 1.76 50.21 µg/mL
80 73.16 ± 2.15
100 80.16 ± 1.07
Ascorbic acid 5 24.92 ± 1.33
10 54.67 ± 2.89
20 68.83 ± 1.68
40 86.73 ± 2.46 3.35 µg/mL
50 91.86 ± 1.75
100 93.63 ± 0.86
Results are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 3); IC 50 = 50% inhibitory concentration. BCAE: aqueous extract of Bombax ceiba
amount of collagen tissue (arrow) stained blue with Masson’s In accordance with earlier reports, [30-32] the present
trichrome stain in the portal triad [Figure 1B]. Liver section of investigations revealed that administration of CCl caused
4
olive oil treated animals [Figure 1A] showed normal hepatic a marked impairment in liver function, as indicated by
architecture with central canal having radiating hepatocytes. significant increase in plasma levels of marker enzymes;
Minimal amount of collagen tissue (arrow) stained blue with and produced extensive histological damages to liver. CCl 4
Masson’s stain was evident in the portal triad. undergoes metabolism in liver to form trichloromethyl
peroxyl (CCl O ) radical and several lines of evidences
[33]
2
3
The BCAE treatment (500 mg/kg) or silymarin showed suggest that the free radicals oxidize the essential
significant protection against CCl -induced hepatic damage macromolecular structures, that is, DNA, proteins, and
4
as indicated by lesser amount of collagen tissue vascular as lipids, and eventually produce cytotoxicity. [34,35] In addition,
compared to vehicle [Figure 1B]. Treatment with 500 mg/kg higher levels of lipid peroxidation are clinically evident in
dose of BCAE exhibited comparable protection [Figure 1D] to liver disorders [36] and the antioxidant therapy was found to
that offered by silymarin (25 mg/kg) [Figure 1C]. ameliorate these effects. [37]
Antioxidant effect of BCAE It was observed that treatment with BCAE ameliorated
Quantitative estimation of antioxidant phytochemicals the CCl -induced impairments in the liver functions except
4
The total flavonoid content of BCAE was found to be 5.79 mg total protein and albumin. BCAE in the dose 500 mg/kg
quercetin equivalents/g of extract, while the total phenolic offered moderate degree of attenuation in the elevated
content was found to be 0.225 mg tannic acid equivalent/g of GOT, GPT, and TG, but with very remarkable prevention
extract, respectively. of ALP and T. The lower dose of 250 mg/kg was almost
ineffective in normalizing the liver markers except for a
DPPH free radical scavenging activity few. BCAE also showed lesser degree of collagen fiber as
The BCAE in concentration range of 10-100 μg/mL inhibited compared to vehicle control [Figure 1] which suggests the
DPPH radical formation as indicated by concentration- preventive nature of the extract on liver tissue fibrosis.
dependent decrease in the purple color of the solution. These findings confirmed that BCAE exerts moderate
Similar effect was obtained with ascorbic acid, the standard hepatoprotective effect. Previously the hepatoprotective
antioxidant, in the concentration range of 5-100 μg/mL. effect of Bombax ceiba flowers was demonstrated in
The linear regression analysis of concentration vs. percent isoniazid plus rifampicin induced hepatotoxicity and
[14]
DPPH inhibition was carried out. The IC value of BCAE and supports the findings of the present study.
50
ascorbic acid, obtained from regression analysis, were 50.21
and 3.35 μg/mL, respectively [Table 3]. Phytochemical analysis of BCAE revealed the presence of
the antioxidant phytochemicals flavonoids, terpenes and
DISCUSSION phenolic compounds. It has been earlier reported that the
flowers and other parts of this plant contains flavonoids
Acute toxicity study of the BCAE (2,000 mg/kg, orally) and sesquiterpenens, etc. [38,39] The present study also
revealed that there was no toxicity of any nature or moribund revealed that BCAE has fair amount of flavonoids and
stage during the observation period. This illustrates that the phenolics.
NOAEL of BCAE is more than 2,000 mg/kg. Based on this, the
BCAE was administered in the dose range of 200 mg/kg (one BCAE was further tested for its antioxidant activity. The
tenth of the limit test dose level). The previous studies results revealed that BCAE has significant free radical
have also used extract of Bombax ceiba in the similar dose scavenging property [Table 3] with IC of 50.21 μg/mL.
50
range. [14] The antioxidant activities of the flavonoids are well
148 Hepatoma Research | Volume 2 | June 1, 2016