Page 156 - Read Online
P. 156
DPPH (1, 1-Diphenyl-2-picryl-hydrazil) free radical scavenging
activity
The free radical scavenging activity of extract was measured
by 1, 1-diphenyl-2-picryl-hydrazil (DPPH•) using the method
[29]
previously described. Briefly, 0.1 mmol/L solution of DPPH
in ethanol was prepared, and 3.5 mL was added to 0.5 mL
of extract solution of different concentrations in water. The
mixture was shaken vigorously and allowed to stand at room
temperature for 30 min. Then the absorbance was measured
at 517 nm by using a spectrophotometer (UV 1800, Shimadzu
Corporation, Japan). Lower absorbance of the reaction
mixture indicated higher free radical scavenging activity.
Ascorbic acid was taken as standard antioxidant. The percent
DPPH scavenging effect was calculated using the following
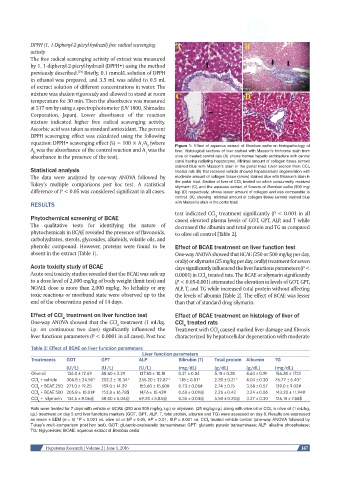
equation: DPPH• scavenging effect (%) = 100 × A /A (where Figure 1: Effect of aqueous extract of Bombax ceiba on histopathology of
1
0
A was the absorbance of the control reaction and A was the liver. Histological sections of liver stained with Masson’s trichrome stain from
1
0
absorbance in the presence of the test). olive oil treated control rats (A) shows normal hepatic architecture with central
canal having radiating hepatocytes. Minimal amount of collagen tissue (arrow)
stained blue with Masson’s stain in the portal triad. Liver section from CCl 4
Statistical analysis treated rats (B) that received vehicle showed hepatocellular degeneration with
The data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by moderate amount of collagen tissue (arrow) stained blue with Masson’s stain in
Tukey’s multiple comparisons post hoc test. A statistical the portal triad. Section of liver of CCl 4 treated rat which concurrently received
silymarin (C) and the aqueous extract of flowers of Bombax ceiba (500 mg/
difference of P < 0.05 was considered significant in all cases. kg) (D) respectively, shows lesser amount of collagen and was comparable to
control (A), showing minimal amount of collagen tissue (arrow) stained blue
RESULTS with Masson’s stain in the portal triad.
test indicated CCl treatment significantly (P < 0.001 in all
4
Phytochemical screening of BCAE cases) elevated plasma levels of GOT, GPT, ALP, and T while
The qualitative tests for identifying the nature of decreased the albumin and total protein and TG as compared
phytochemicals in BCAE revealed the presence of flavonoids, to olive oil control [Table 2].
carbohydrates, sterols, glycosides, alkaloids, volatile oils, and
phenolic compound. However, proteins were found to be Effect of BCAE treatment on liver function test
absent in the extract [Table 1]. One-way ANOVA showed that BCAE (250 or 500 mg/kg per day,
orally) or silymarin (25 mg/kg per day, orally) treatment for seven
Acute toxicity study of BCAE days significantly influenced the liver functions parameters (P <
Acute oral toxicity studies revealed that the BCAE was safe up 0.0001) in CCl treated rats. The BCAE or silymarin significantly
4
to a dose level of 2,000 mg/kg of body weight (limit test) and (P < 0.05-0.001) attenuated the elevation in levels of GOT, GPT,
NOAEL dose is more than 2,000 mg/kg. No lethality or any ALP, T, and TG while increased total protein without affecting
toxic reactions or moribund state were observed up to the the levels of albumin [Table 2]. The effect of BCAE was lesser
end of the observation period of 14 days. than that of standard drug silymarin.
Effect of CCl treatment on liver function test Effect of BCAE treatment on histology of liver of
4
One-way ANOVA showed that the CCl treatment (1 mL/kg, CCl treated rats
4
4
i.p. on continuous two days) significantly influenced the Treatment with CCl caused marked liver damage and fibrosis
4
liver functions parameters (P < 0.0001 in all cases). Post hoc characterized by hepatocellular degeneration with moderate
Table 2: Effect of BCAE on liver function parameters
Liver function parameters
Treatments GOT GPT ALP Bilirubin (T) Total protein Albumin TG
(U/L) (U/L) (U/L) (mg/dL) (g/dL) (g/dL) (mg/dL)
Olive oil 134.0 ± 12.69 48.60 ± 2.29 137.80 ± 10.18 0.21 ± 0.04 5.10 ± 0.30 4.64 ± 0.19 156.30 ± 17.01
CCl + vehicle 306.8 ± 24.50* 202.2 ± 10.34* 255.20 ± 32.87* 1.18 ± 0.01* 2.30 ± 0.21* 4.04 ± 0.30 76.77 ± 6.40*
4
CCl + BCAE 250 271.0 ± 19.25 189.0 ± 14.39 155.60 ± 15.60# 0.73 ± 0.06# 2.74 ± 0.15 3.58 ± 0.57 139.0 ± 9.02#
4
CCl + BCAE 500 205.8 ± 10.01# 153.8 ± 16.78$ 147.6 ± 15.42# 0.60 ± 0.09@ 2.26 ± 0.42 3.24 ± 0.06 143.20 ± 11.94#
4
CCl + silymarin 134.6 ± 8.06@ 58.00 ± 5.04@ 69.20 ± 5.85@ 0.35 ± 0.04@ 5.50 ± 0.20@ 3.27 ± 0.30 126.10 ± 7.88$
4
Rats were treated for 7 days with vehicle or BCAE (250 and 500 mg/kg, i.g.) or silymarin (25 mg/kg i.g.) along with olive oil or CCl 4 in olive oil (1 mL/kg,
i.p.) treatment on day 5 and liver functions markers (GOT, GPT, ALP, T, total protein, albumin and TG) were assessed on day 8. Results are expressed
as mean ± SEM (n = 5) *P < 0.001 vs. olive oil or $P < 0.05, #P < 0.01, @P < 0.001 vs. CCl 4 treated vehicle control (one-way ANOVA followed by
Tukey’s multi-comparison post hoc test). GOT: glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase; GPT: glutamic pyruvic transaminase; ALP: alkaline phosphatase;
TG: triglycerides; BCAE: aqueous extract of Bombax ceiba
Hepatoma Research | Volume 2 | June 1, 2016 147