Page 214 - Read Online
P. 214
Page 575 Loh et al. Extracell Vesicles Circ Nucleic Acids 2023;4:568-87 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/evcna.2023.34
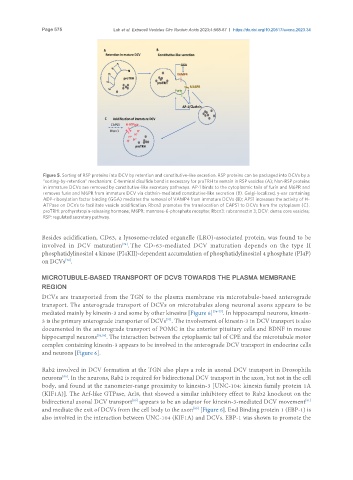
Figure 5. Sorting of RSP proteins into DCV by retention and constitutive-like secretion. RSP proteins can be packaged into DCVs by a
“sorting-by-retention” mechanism: C-terminal disulfide bond is necessary for proTRH to remain in RSP vesicles (A); Non-RSP proteins
in immature DCVs are removed by constitutive-like secretory pathways. AP-1 binds to the cytoplasmic tails of furin and M6PR and
removes furin and M6PR from immature DCV via clathrin-mediated constitutive-like secretion (B). Golgi-localized, γ-ear containing
ADP-ribosylation factor binding (GGA) mediates the removal of VAMP4 from immature DCVs (B); APS1 increases the activity of H-
ATPase on DCVs to facilitate vesicle acidification. Rbcn3 promotes the translocation of CAPS1 to DCVs from the cytoplasm (C).
proTRH: prothyrotropin-releasing hormone; M6PR: mannose-6-phosphate receptor; Rbcn3: rabconnectin 3; DCV: dense core vesicles;
RSP: regulated secretory pathway.
Besides acidification, CD63, a lysosome-related organelle (LRO)-associated protein, was found to be
involved in DCV maturation . The CD-63-mediated DCV maturation depends on the type II
[73]
phosphatidylinositol 4 kinase (PI4KII)-dependent accumulation of phosphatidylinositol 4 phosphate (PI4P)
on DCVs .
[73]
MICROTUBULE-BASED TRANSPORT OF DCVS TOWARDS THE PLASMA MEMBRANE
REGION
DCVs are transported from the TGN to the plasma membrane via microtubule-based anterograde
transport. The anterograde transport of DCVs on microtubules along neuronal axons appears to be
mediated mainly by kinesin-3 and some by other kinesins [Figure 6] [74-77] . In hippocampal neurons, kinesin-
3 is the primary anterograde transporter of DCVs . The involvement of kinesin-3 in DCV transport is also
[77]
documented in the anterograde transport of POMC in the anterior pituitary cells and BDNF in mouse
hippocampal neurons [78,79] . The interaction between the cytoplasmic tail of CPE and the microtubule motor
complex containing kinesin-3 appears to be involved in the anterograde DCV transport in endocrine cells
and neurons [Figure 6].
Rab2 involved in DCV formation at the TGN also plays a role in axonal DCV transport in Drosophila
neurons . In the neurons, Rab2 is required for bidirectional DCV transport in the axon, but not in the cell
[80]
body, and found at the nanometer-range proximity to kinesin-3 [UNC-104: kinesin family protein 1A
(KIF1A)]. The Arf-like GTPase, Arl8, that showed a similar inhibitory effect to Rab2 knockout on the
[80]
[81]
bidirectional axonal DCV transport appears to be an adaptor for kinesin-3-mediated DCV movement
[80]
and mediate the exit of DCVs from the cell body to the axon [Figure 6]. End Binding protein 1 (EBP-1) is
also involved in the interaction between UNC-104 (KIF1A) and DCVs. EBP-1 was shown to promote the