Page 40 - Read Online
P. 40
Page 12 of 24 Boaretto et al. Energy Mater. 2025, 5, 500040 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/energymater.2024.203
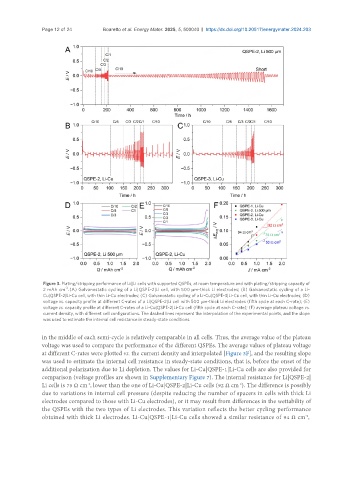
Figure 3. Plating/stripping performance of Li||Li cells with supported QSPEs, at room temperature and with plating/stripping capacity of
-2
2 mAh cm . (A) Galvanostatic cycling of a Li|QSPE-2|Li cell, with 500 µm-thick Li electrodes; (B) Galvanostatic cycling of a Li-
Cu|QSPE-2|Li-Cu cell, with thin Li-Cu electrodes; (C) Galvanostatic cycling of a Li-Cu|QSPE-3|Li-Cu cell, with thin Li-Cu electrodes; (D)
voltage vs. capacity profile at different C-rates of a Li|QSPE-2|Li cell with 500 µm-thick Li electrodes (fifth cycle at each C-rate); (E)
voltage vs. capacity profile at different C-rates of a Li-Cu|QSPE-2|Li-Cu cell (fifth cycle at each C-rate); (F) average plateau voltage vs.
current density, with different cell configurations. The dashed lines represent the interpolation of the experimental points, and the slope
was used to estimate the internal cell resistance in steady-state conditions.
in the middle of each semi-cycle is relatively comparable in all cells. Thus, the average value of the plateau
voltage was used to compare the performance of the different QSPEs. The average values of plateau voltage
at different C-rates were plotted vs. the current density and interpolated [Figure 3F], and the resulting slope
was used to estimate the internal cell resistance in steady-state conditions, that is, before the onset of the
additional polarization due to Li depletion. The values for Li-Cu|QSPE-1|Li-Cu cells are also provided for
comparison (voltage profiles are shown in Supplementary Figure 7). The internal resistance for Li|QSPE-2|
Li cells is 75 Ω cm , lower than the one of Li-Cu|QSPE-2|Li-Cu cells (92 Ω cm ). The difference is possibly
-2
-2
due to variations in internal cell pressure (despite reducing the number of spacers in cells with thick Li
electrodes compared to those with Li-Cu electrodes), or it may result from differences in the wettability of
the QSPEs with the two types of Li electrodes. This variation reflects the better cycling performance
-2
obtained with thick Li electrodes. Li-Cu|QSPE-1|Li-Cu cells showed a similar resistance of 94 Ω cm ,