Page 35 - Read Online
P. 35
Page 28 of 35 Zhang et al. Chem Synth 2023;3:10 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cs.2022.40
Table 3. Summary of commercial application prospects of various materials for psaAWH
Material Stability Recyclability Toxicity 1 Large-scale production
Zeolites High stability high-temperature Most are non-toxic Already used for
regeneration commercialization
MOFs Meet the needs of Yes Toxicity mainly comes from some Can be large-scale produced
psaAWH metals
COFs Meet the needs of Yes uncertain No
psaAWH
Hydrogels Meet the needs of Yes Most are non-toxic Already used for
psaAWH commercialization
Porous Meet the needs of Yes Most are non-toxic No
carbons psaAWH
CPOSs Meet the needs of Yes uncertain Can be large-scale produced
psaAWH
1
Toxicity refers to the harmful effects on human body or cells. COFs: Covalent organic frameworks; CPOSs: crystalline porous organic salts; MOFs:
metal-organic frameworks.
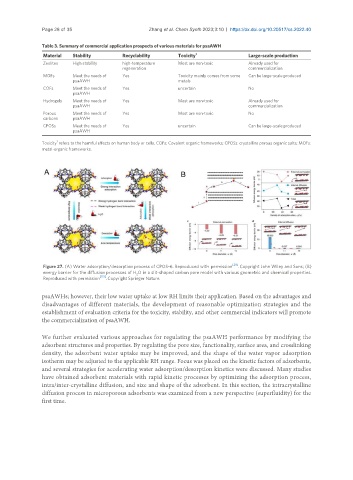
Figure 27. (A) Water adsorption/desorption process of CPOS-6. Reproduced with permission [29] . Copyright John Wiley and Sons; (B)
energy barrier for the diffusion processes of H O in a slit-shaped carbon pore model with various geometric and chemical properties.
2
Reproduced with permission [151] . Copyright Springer Nature.
psaAWHs; however, their low water uptake at low RH limits their application. Based on the advantages and
disadvantages of different materials, the development of reasonable optimization strategies and the
establishment of evaluation criteria for the toxicity, stability, and other commercial indicators will promote
the commercialization of psaAWH.
We further evaluated various approaches for regulating the psaAWH performance by modifying the
adsorbent structures and properties. By regulating the pore size, functionality, surface area, and crosslinking
density, the adsorbent water uptake may be improved, and the shape of the water vapor adsorption
isotherm may be adjusted to the applicable RH range. Focus was placed on the kinetic factors of adsorbents,
and several strategies for accelerating water adsorption/desorption kinetics were discussed. Many studies
have obtained adsorbent materials with rapid kinetic processes by optimizing the adsorption process,
intra/inter-crystalline diffusion, and size and shape of the adsorbent. In this section, the intracrystalline
diffusion process in microporous adsorbents was examined from a new perspective (superfluidity) for the
first time.