Page 22 - Read Online
P. 22
Zhang et al. Chem Synth 2023;3:10 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cs.2022.40 Page 15 of 35
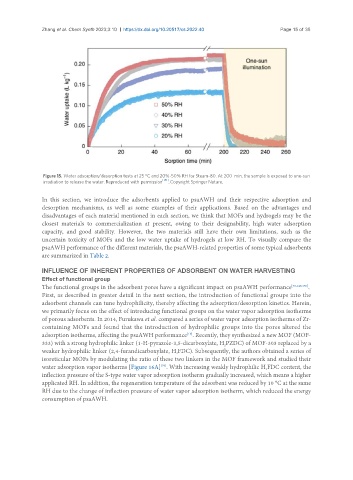
Figure 15. Water adsorption/desorption tests at 25 °C and 20%-50% RH for Steam-80. At 200 min, the sample is exposed to one-sun
irradiation to release the water. Reproduced with permission [151] . Copyright Springer Nature.
In this section, we introduce the adsorbents applied to psaAWH and their respective adsorption and
desorption mechanisms, as well as some examples of their applications. Based on the advantages and
disadvantages of each material mentioned in each section, we think that MOFs and hydrogels may be the
closest materials to commercialization at present, owing to their designability, high water adsorption
capacity, and good stability. However, the two materials still have their own limitations, such as the
uncertain toxicity of MOFs and the low water uptake of hydrogels at low RH. To visually compare the
psaAWH performance of the different materials, the psaAWH-related properties of some typical adsorbents
are summarized in Table 2.
INFLUENCE OF INHERENT PROPERTIES OF ADSORBENT ON WATER HARVESTING
Effect of functional group
The functional groups in the adsorbent pores have a significant impact on psaAWH performance [78,149,150] .
First, as described in greater detail in the next section, the introduction of functional groups into the
adsorbent channels can tune hydrophilicity, thereby affecting the adsorption/desorption kinetics. Herein,
we primarily focus on the effect of introducing functional groups on the water vapor adsorption isotherms
of porous adsorbents. In 2014, Furukawa et al. compared a series of water vapor adsorption isotherms of Zr-
containing MOFs and found that the introduction of hydrophilic groups into the pores altered the
adsorption isotherms, affecting the psaAWH performance . Recently, they synthesized a new MOF (MOF-
[19]
333) with a strong hydrophilic linker (1-H-pyrazole-3,5-dicarboxylate, H PZDC) of MOF-303 replaced by a
2
weaker hydrophilic linker (2,4-furandicarboxylate, H FDC). Subsequently, the authors obtained a series of
2
isoreticular MOFs by modulating the ratio of these two linkers in the MOF framework and studied their
water adsorption vapor isotherms [Figure 16A] . With increasing weakly hydrophilic H FDC content, the
[79]
2
inflection pressure of the S-type water vapor adsorption isotherm gradually increased, which means a higher
applicated RH. In addition, the regeneration temperature of the adsorbent was reduced by 10 °C at the same
RH due to the change of inflection pressure of water vapor adsorption isotherm, which reduced the energy
consumption of psaAWH.