Page 66 - Read Online
P. 66
Page 10 of 20 Huang et al. Complex Eng Syst 2023;3:2 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ces.2022.43
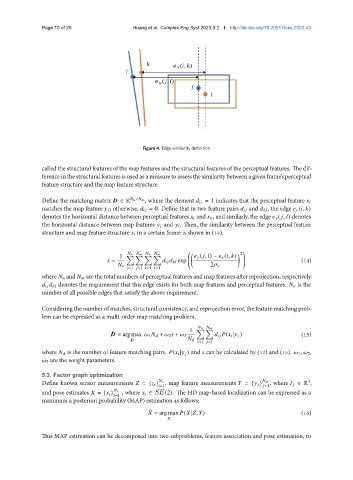
Figure 4. Edge similarity definition
called the structural features of the map features and the structural features of the perceptual features. The dif-
ference in the structural featuresis used as a measure to assessthe similarity between a givenframe’s perceptual
feature structure and the map feature structure.
Define the matching matrix ∈ R × , where the element = 1 indicates that the perceptual feature
matches the map feature ; otherwise, = 0. Define that in two feature pairs and , the edge ( , )
denotes the horizontal distance between perceptual features and , and similarly, the edge ( , ) denotes
the horizontal distance between map features and . Then, the similarity between the perceptual feature
structure and map feature structure in a certain frame is shown in (14).
2 !
1 Õ Õ Õ Õ ( , ) − ( , )
= exp (14)
2
=1 =1 =1 =1
where and are the total numbers of perceptual features and map features after reprojection, respectively.
denotes the requirement that this edge exists for both map features and perceptual features. is the
number of all possible edges that satisfy the above requirement.
Considering the number of matches, structural consistency, and reprojection error, the feature matching prob-
lem can be expressed as a multi-order map matching problem.
1 Õ Õ
ˆ (15)
= arg max 1 + 2 + 3 ( | )
=1 =1
where is the number of feature matching pairs. ( | ) and can be calculated by (12) and (15). 1, 2,
3 are the weight parameters.
5.3. Factor graph optimization
Define known sensor measurements = { } , map feature measurements = { } , where ∈ R ,
3
=1 =1
, where ∈ SE (2). The HD map-based localization can be expressed as a
and pose estimates = { }
=1
maximum a posteriori probability (MAP) estimation as follows:
ˆ (16)
= arg max ( | , )
This MAP estimation can be decomposed into two subproblems, feature association and pose estimation, to