Page 148 - Read Online
P. 148
Qin et al. Microstructures 2023;3:2023035 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/microstructures.2023.34 Page 7 of 11
Table 3. The values of R and C for each component at 325 °C derived based on the Z" and M"/ε peak values for -0.01 ≤ x ≤ 0.04
0
Component 1 (grain boundary) Component 2 (shell) Component 3 (core)
Composition R = 2 Z'' C = 1/(4πfZ'') R = M''/(ε πf) C = ε /(2M'') R = M''/(ε πf) C = ε /(2 M'')
0
0
0
0
-1
-1
-1
(kΩ·cm) (F cm ) (kΩ·cm) (F cm ) (kΩ·cm) (F cm )
-10 -10 -9
-0.01 (325 °C) 346 5.73 × 10 281 4.65 × 10 0.82 1.42 × 10
0.00 (325 °C) 393 6.07 × 10 -10 315 4.77 × 10 -10 1.08 1.30 × 10 -9
-10 -10 -9
0.01 (325 °C) 474 3.48 × 10 378 2.88 × 10 0.95 1.06 × 10
-10 -10 -9
0.02 (325 °C) 438 5.45 × 10 329 4.16 × 10 1.12 1.14 × 10
0.03 (325 °C) 314 5.25 × 10 -10 230 3.93 × 10 -10 0.99 1.08 × 10 -9
-10 -10 -9
0.04 (325 °C) 334 5.41 × 10 245 4.03 × 10 1.07 1.09 × 10
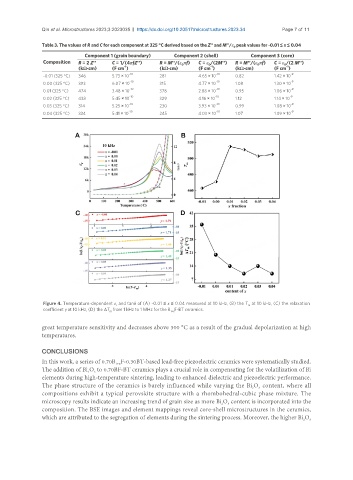
Figure 4. Temperature-dependent ε and tanδ of (A) -0.01 ≤ x ≤ 0.04 measured at 10 kHz, (B) the T at 10 kHz, (C) the relaxation
r m
coefficient γ at 10 kHz, (D) the ΔT from 1 kHz to 1 MHz for the B F-BT ceramics.
m 1+x
great temperature sensitivity and decreases above 300 °C as a result of the gradual depolarization at high
temperatures.
CONCLUSIONS
In this work, a series of 0.70B F-0.30BT-based lead-free piezoelectric ceramics were systematically studied.
1+x
The addition of Bi O to 0.70BF-BT ceramics plays a crucial role in compensating for the volatilization of Bi
2
3
elements during high-temperature sintering, leading to enhanced dielectric and piezoelectric performance.
The phase structure of the ceramics is barely influenced while varying the Bi O content, where all
2
3
compositions exhibit a typical perovskite structure with a rhombohedral-cubic phase mixture. The
microscopy results indicate an increasing trend of grain size as more Bi O content is incorporated into the
2
3
composition. The BSE images and element mappings reveal core-shell microstructures in the ceramics,
which are attributed to the segregation of elements during the sintering process. Moreover, the higher Bi O
3
2