Page 28 - Read Online
P. 28
Page 8 of 15 Ying et al. Microstructures 2023;3:2023018 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/microstructures.2022.47
Table 2. Elastic moduli of different (hkl) planes in FCC and Cr B-type phases
2
FCC phase Cr B-type phase
2
E /GPa E 200 /GPa E 220 /GPa E /GPa E 002 /GPa E /GPa E 202 /GPa
111
311
112
244 ± 7 160 ± 4 222 ± 8 197 ± 2 168 ± 4 190 ± 4 229 ± 8
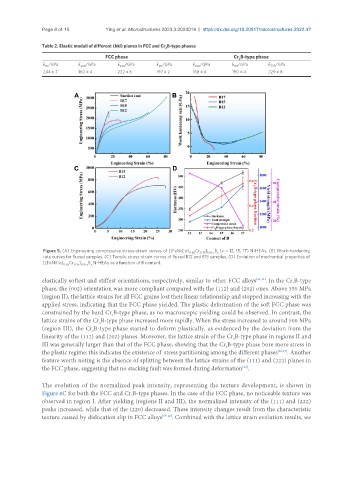
Figure 5. (A) Engineering compressive stress-strain curves of [(FeNiCo) 0.85 Cr 0.15 100-x x
]
B (x = 12, 15, 17) N-HEAs. (B) Work-hardening
rate curves for fluxed samples. (C) Tensile stress-strain curves of fluxed B12 and B15 samples. (D) Evolution of mechanical properties of
[(FeNiCo) 0.85 Cr 0.15 100-x x
B N-HEAs as a function of B content.
]
elastically softest and stiffest orientations, respectively, similar to other FCC alloys [34,35] . In the Cr B-type
2
phase, the (002) orientation was more compliant compared with the (112) and (202) ones. Above 350 MPa
(region II), the lattice strains for all FCC grains lost their linear relationship and stopped increasing with the
applied stress, indicating that the FCC phase yielded. The plastic deformation of the soft FCC phase was
constrained by the hard Cr B-type phase, as no macroscopic yielding could be observed. In contrast, the
2
lattice strains of the Cr B-type phase increased more rapidly. When the stress increased to around 500 MPa
2
(region III), the Cr B-type phase started to deform plastically, as evidenced by the deviation from the
2
linearity of the (112) and (202) planes. Moreover, the lattice strain of the Cr B-type phase in regions II and
2
III was generally larger than that of the FCC phase, showing that the Cr B-type phase bore more stress in
2
the plastic regime; this indicates the existence of stress partitioning among the different phases [36,37] . Another
feature worth noting is the absence of splitting between the lattice strains of the (111) and (222) planes in
the FCC phase, suggesting that no stacking fault was formed during deformation .
[38]
The evolution of the normalized peak intensity, representing the texture development, is shown in
Figure 6C for both the FCC and Cr B-type phases. In the case of the FCC phase, no noticeable texture was
2
observed in region I. After yielding (regions II and III), the normalized intensity of the (111) and (222)
peaks increased, while that of the (220) decreased. These intensity changes result from the characteristic
texture caused by dislocation slip in FCC alloys [39-42] . Combined with the lattice strain evolution results, we