Page 47 - Read Online
P. 47
Todua et al. Homocysteine in pulmonary artery thromboembolism
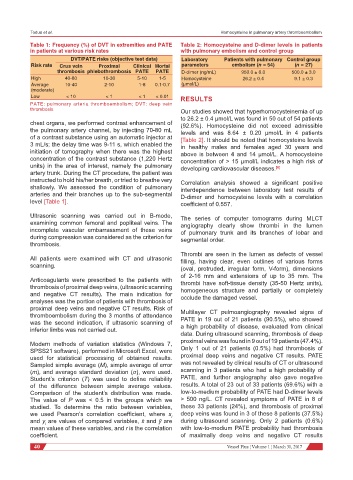
Table 1: Frequency (%) of DVT in extremities and PATE Table 2: Homocysteine and D-dimer levels in patients
in patients at various risk rates with pulmonary embolism and control group
DVT/PATE risks (objective test data) Laboratory Patients with pulmonary Control group
Risk rate Crus vein Proximal Clinical Mortal parameters embolism (n = 54) (n = 27)
thrombosis phlebothrombosis PATE PATE D-dimer (ng/mL) 950.0 ± 6.0 500.0 ± 3.0
High 40-80 10-30 5-10 1-5 Homocysteine 26.2 ± 0.4 9.1 ± 0.3
Average 10-40 2-10 1-8 0.1-0.7 (μmol/L)
(moderate)
Low < 10 < 1 < 1 < 0.01 RESULTS
PATE: pulmonary arteria thromboembolism; DVT: deep vein
thrombosis Our studies showed that hyperhomocysteinemia of up
to 26.2 ± 0.4 μmol/L was found in 50 out of 54 patients
chest organs, we performed contrast enhancement of (92.6%). Homocysteine did not exceed admissible
the pulmonary artery channel, by injecting 70-80 mL levels and was 8.64 ± 0.20 μmol/L in 4 patients
of a contrast substance using an automatic injector at [Table 2]. It should be noted that homocysteine levels
3 mL/s; the delay time was 9-11 s, which enabled the in healthy males and females aged 30 years and
initiation of tomography when there was the highest above is between 4 and 14 μmol/L. A homocysteine
concentration of the contrast substance (1,220 Hertz concentration of > 15 μmol/L indicates a high risk of
units) in the area of interest, namely the pulmonary developing cardiovascular diseases. [6]
artery trunk. During the CT procedure, the patient was
instructed to hold his/her breath, or tried to breathe very Correlation analysis showed a significant positive
shallowly. We assessed the condition of pulmonary interdependence between laboratory test results of
arteries and their branches up to the sub-segmental D-dimer and homocysteine levels with a correlation
level [Table 1]. coefficient of 0.557.
Ultrasonic scanning was carried out in В-mode, The series of computer tomograms during МLCТ
examining common femoral and popliteal veins. The angiography clearly show thrombi in the lumen
incomplete vascular embarrassment of these veins of pulmonary trunk and its branches of lobar and
during compression was considered as the criterion for segmental order.
thrombosis.
Thrombi are seen in the lumen as defects of vessel
All patients were examined with CT and ultrasonic filling, having clear, even outlines of various forms
scanning.
(oval, protruded, irregular form, V-form), dimensions
of 2-16 mm and extensions of up to 35 mm. The
Anticoagulants were prescribed to the patients with thrombi have soft-tissue density (35-50 Hertz units),
thrombosis of proximal deep veins, (ultrasonic scanning homogeneous structure and partially or completely
and negative CT results). The main indication for occlude the damaged vessel.
analyses was the portion of patients with thrombosis of
proximal deep veins and negative CT results. Risk of
thromboembolism during the 3 months of attendance Multilayer CT pulmoangiography revealed signs of
was the second indication, if ultrasonic scanning of PATE in 19 out of 21 patients (90.5%), who showed
inferior limbs was not carried out. a high probability of disease, evaluated from clinical
data. During ultrasound scanning, thrombosis of deep
Modern methods of variation statistics (Windows 7, proximal veins was found in 9 out of 19 patients (47.4%).
SPSS21 software), performed in Microsoft Excel, were Only 1 out of 21 patients (0.5%) had thrombosis of
used for statistical processing of obtained results. proximal deep veins and negative CT results. PATE
Sampled simple average (M), simple average of error was not revealed by clinical results of CT or ultrasound
(m), and average standard deviation (σ), were used. scanning in 3 patients who had a high probability of
Student’s criterion (T) was used to define reliability PATE, and further angiography also gave negative
of the difference between simple average values. results. A total of 23 out of 33 patients (69.6%) with a
Comparison of the student’s distribution was made. low-to-medium probability of PATE had D-dimer levels
The value of P was < 0.5 in the groups which we > 500 ng/L. CT revealed symptoms of PATE in 8 of
studied. To determine the ratio between variables, these 33 patients (24%), and thrombosis of proximal
we used Pearson’s correlation coefficient, where x i deep veins was found in 3 of these 8 patients (37.5%)
and y are values of compared variables, x and ӯ are during ultrasound scanning. Only 2 patients (0.6%)
i
mean values of these variables, and r is the correlation with low-to-medium PATE probability had thrombosis
coefficient. of maximally deep veins and negative CT results
40 Vessel Plus ¦ Volume 1 ¦ March 31, 2017