Page 244 - Read Online
P. 244
Martínez et al. Cardiomyocyte energetic changes in ischemia and arrythmogenesis
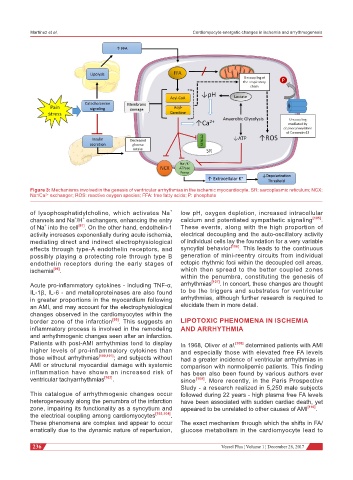
Figure 3: Mechanisms involved in the genesis of ventricular arrhythmias in the ischemic myocardiocyte. SR: sarcoplasmic reticulum; NCX:
2+
+
Na /Ca exchanger; ROS: reactive oxygen species; FFA: free fatty acids; P: phosphate
+
of lysophosphatidylcholine, which activates Na low pH, oxygen depletion, increased intracellular
+
+
channels and Na /H exchangers, enhancing the entry calcium and potentiated sympathetic signaling [105] .
+
of Na into the cell [97] . On the other hand, endothelin-1 These events, along with the high proportion of
activity increases exponentially during acute ischemia, electrical decoupling and the auto-oscillatory activity
mediating direct and indirect electrophysiological of individual cells lay the foundation for a very variable
effects through type-A endothelin receptors, and syncytial behavior [106] . This leads to the continuous
possibly playing a protecting role through type B generation of mini-reentry circuits from individual
endothelin receptors during the early stages of ectopic rhythmic foci within the decoupled cell areas,
ischemia [98] . which then spread to the better coupled zones
within the penumbra, constituting the genesis of
Acute pro-inflammatory cytokines - including TNF-α, arrhythmias [107] . In concert, these changes are thought
IL-1β, IL-6 - and metalloproteinases are also found to be the triggers and substrates for ventricular
in greater proportions in the myocardium following arrhythmias, although further research is required to
an AMI, and may account for the electrophysiological elucidate them in more detail.
changes observed in the cardiomyocytes within the
border zone of the infarction [99] . This suggests an LIPOTOXIC PHENOMENA IN ISCHEMIA
inflammatory process is involved in the remodeling AND ARRHYTHMIA
and arrhythmogenic changes seen after an infarction.
Patients with post-AMI arrhythmias tend to display In 1968, Oliver et al. [108] determined patients with AMI
higher levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines than and especially those with elevated free FA levels
those without arrhythmias [100,101] ; and subjects without had a greater incidence of ventricular arrhythmias in
AMI or structural myocardial damage with systemic comparison with normolipemic patients. This finding
inflammation have shown an increased risk of has been also been found by various authors ever
ventricular tachyarrhythmias [102] . since [109] . More recently, in the Paris Prospective
Study - a research realized in 5,250 male subjects
This catalogue of arrhythmogenic changes occur followed during 22 years - high plasma free FA levels
heterogeneously along the penumbra of the infarction have been associated with sudden cardiac death, yet
zone, impairing its functionality as a syncytium and appeared to be unrelated to other causes of AMI [110] .
the electrical coupling among cardiomyocytes [103,104] .
These phenomena are complex and appear to occur The exact mechanism through which the shifts in FA/
erratically due to the dynamic nature of reperfusion, glucose metabolism in the cardiomyocyte lead to
236 Vessel Plus ¦ Volume 1 ¦ December 28, 2017