Page 239 - Read Online
P. 239
Martínez et al. Cardiomyocyte energetic changes in ischemia and arrythmogenesis
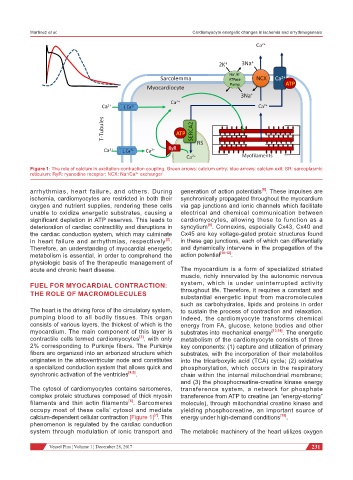
Figure 1: The role of calcium in excitation-contraction coupling. Green arrows: calcium entry; blue arrows: calcium exit; SR: sarcoplasmic
reticulum; RyR: ryanodine receptor; NCX: Na /Ca exchanger
2+
+
arrhythmias, heart failure, and others. During generation of action potentials . These impulses are
[8]
ischemia, cardiomyocytes are restricted in both their synchronically propagated throughout the myocardium
oxygen and nutrient supplies, rendering these cells via gap junctions and ionic channels which facilitate
unable to oxidize energetic substrates, causing a electrical and chemical communication between
significant depletion in ATP reserves. This leads to cardiomyocytes, allowing these to function as a
[9]
deterioration of cardiac contractility and disruptions in syncytium . Connexins, especially Cx43, Cx40 and
the cardiac conduction system, which may culminate Cx45 are key voltage-gated proteic structures found
[2]
in heart failure and arrhythmias, respectively . in these gap junctions, each of which can differentially
Therefore, an understanding of myocardial energetic and dynamically intervene in the propagation of the
metabolism is essential, in order to comprehend the action potential [10-12] .
physiologic basis of the therapeutic management of
acute and chronic heart disease. The myocardium is a form of specialized striated
muscle, richly innervated by the autonomic nervous
FUEL FOR MYOCARDIAL CONTRACTION: system, which is under uninterrupted activity
THE ROLE OF MACROMOLECULES throughout life. Therefore, it requires a constant and
substantial energetic input from macromolecules
such as carbohydrates, lipids and proteins in order
The heart is the driving force of the circulatory system, to sustain the process of contraction and relaxation.
pumping blood to all bodily tissues. This organ Indeed, the cardiomyocyte transforms chemical
consists of various layers, the thickest of which is the energy from FA, glucose, ketone bodies and other
myocardium. The main component of this layer is substrates into mechanical energy [13,14] . The energetic
contractile cells termed cardiomyocytes , with only metabolism of the cardiomyocyte consists of three
[3]
2% corresponding to Purkinje fibers. The Purkinje key components: (1) capture and utilization of primary
fibers are organized into an arborized structure which substrates, with the incorporation of their metabolites
originates in the atrioventricular node and constitutes into the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle; (2) oxidative
a specialized conduction system that allows quick and phosphorylation, which occurs in the respiratory
synchronic activation of the ventricles [4,5] . chain within the internal mitochondrial membrane;
and (3) the phosphocreatine-creatine kinase energy
The cytosol of cardiomyocytes contains sarcomeres, transference system, a network for phosphate
complex proteic structures composed of thick myosin transference from ATP to creatine (an “energy-storing”
[6]
filaments and thin actin filaments . Sarcomeres molecule), through mitochondrial creatine kinase and
occupy most of these cells’ cytosol and mediate yielding phosphocreatine, an important source of
calcium-dependent cellular contraction [Figure 1] . This energy under high-demand conditions [15] .
[7]
phenomenon is regulated by the cardiac conduction
system through modulation of ionic transport and The metabolic machinery of the heart utilizes oxygen
Vessel Plus ¦ Volume 1 ¦ December 28, 2017 231