Page 117 - Read Online
P. 117
Alipov et al. Difference between native and desialylated LDL
90
80
70
60
Protein (nmole/mg) 50 Galactose
Mannose
40
N-acetyl glucosamine
30
Sialic acid
20
10
0
Native LDL of Desialylated Native LDL Desialylated
healthy donors LDL of healthy of patients LDL of patients
donors
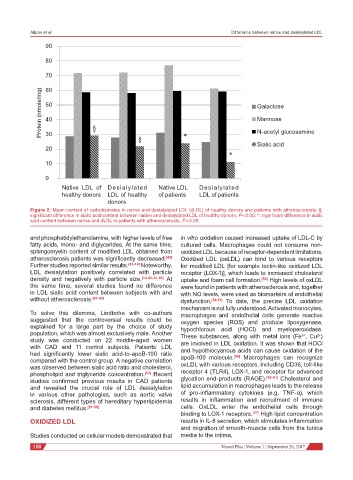
Figure 2: Mean content of carbohydrates in native and desialylated LDL (dLDL) of healthy donors and patients with atherosclerosis; §:
significant difference in sialic acid content between native and desialylated LDL of healthy donors, P < 0.05; *: significant difference in sialic
acid content between native and dLDL in patients with atherosclerosis, P < 0.05
and phosphatidylethanolamine, with higher levels of free in vitro oxidation caused increased uptake of LDL-C by
fatty acids, mono- and diglycerides. At the same time, cultured cells. Macrophages could not consume non-
sphingomyelin content of modified LDL obtained from oxidized LDL because of receptor-dependent limitations.
atherosclerosis patients was significantly decreased. [40] Oxidized LDL (oxLDL) can bind to various receptors
Further studies reported similar results. [42-44] Noteworthy, for modified LDL [for example lectin-like oxidized LDL
LDL desialylation positively correlated with particle receptor (LOX-1)], which leads to increased cholesterol
density and negatively with particle size. [14,40,43-46] At uptake and foam cell formation. [56] High levels of oxLDL
the same time, several studies found no difference were found in patients with atherosclerosis and, together
in LDL sialic acid content between subjects with and with NO levels, were used as biomarkers of endothelial
without atherosclerosis. [47-49] dysfunction. [56,57] To date, the precise LDL oxidation
mechanism is not fully understood. Activated monocytes,
To solve this dilemma, Lindbohn with co-authors macrophages and endothelial cells generate reactive
suggested that the controversial results could be oxygen species (ROS) and produce lipoxygenase,
explained for a large part by the choice of study hypochlorous acid (HOCl) and myeloperoxidase.
population, which was almost exclusively male. Another These substances, along with metal ions (Fe , Cu )
2+
3+
study was conducted on 22 middle-aged women are involved in LDL oxidation. It was shown that HOCl
with CAD and 11 control subjects. Patients’ LDL and hypothiocyanous acids can cause oxidation of the
had significantly lower sialic acid-to-apoB-100 ratio [58]
compared with the control group. A negative correlation apoB-100 molecule. Macrophages can recognize
was observed between sialic acid ratio and cholesterol, oxLDL with various receptors, including CD36, toll-like
phospholipid and triglyceride concentration. [50] Recent receptor 4 (TLR4), LOX-1, and receptor for advanced
[59-61]
studies confirmed previous results in CAD patients glycation end-products (RAGE). Cholesterol and
and revealed the crucial role of LDL desialylation lipid accumulation in macrophages leads to the release
in various other pathologies, such as aortic valve of pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g. TNF-α), which
sclerosis, different types of hereditary hyperlipidemia results in inflammation and recruitment of immune
and diabetes mellitus. [51-55] cells. OxLDL enter the endothelial cells through
binding to LOX-1 receptors. [61] High lipid concentration
OXIDIZED LDL results in IL-8 secretion, which stimulates inflammation
and migration of smooth-muscle cells from the tunica
Studies conducted on cellular models demonstrated that media to the intima.
110 Vessel Plus ¦ Volume 1 ¦ September 26, 2017